HydPy-G-GR6 (Génie Rural model with 6 parameters)¶
The GR6J model (modèle du Génie Rural à 6 parametres Journalier) is a daily
lumped six-parameter rainfall-runoff model and belongs to the family of soil moisture
accounting models. It was published by Pushpalatha et al. (2011) and is a
modification of GR4 and GR5. Our implementation, gland_gr6, follows the one of the R
package airGR (Coron et al., 2017) but with a few extensions that we explain in the
documentation of gland_gr4, which implements and extends GR4J.
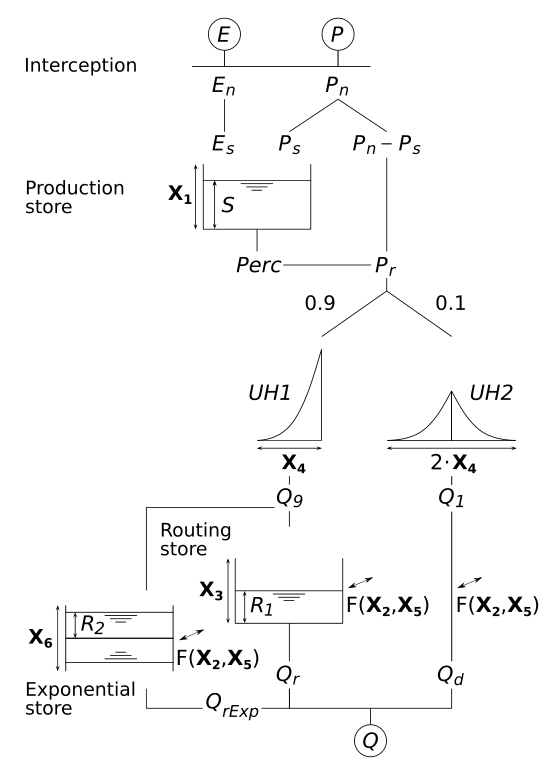
GR6J resembles GR4J in the simulation of runoff concentration (two Unit Hydrographs instead of one) and GR5J in the calculation of groundwater exchange (additional parameter X5). Its unique feature is an exponential store that is connected the new parameter X6.
The following figure (Coron et al., 2023) shows the general structure of
gland_gr6:
Integration tests¶
Note
When new to HydPy, consider reading section Integration Tests first.
The settings of the following tests are similar to the ones of the application models
gland_gr4 and gland_gr5. Hence, comparing the test results gives a good impression
of the functional differences between the three models.
The following settings are identical:
>>> from hydpy import pub
>>> pub.timegrids = "1990-01-01", "1990-02-20", "1d"
>>> from hydpy.models.gland_gr6 import *
>>> parameterstep("1d")
>>> from hydpy import Element
>>> land = Element("land", outlets="outlet")
>>> land.model = model
>>> area(360.0)
>>> with model.add_petmodel_v1("evap_ret_io"):
... evapotranspirationfactor(1.0)
>>> from hydpy import IntegrationTest
>>> test = IntegrationTest(land)
>>> test.plotting_options.axis1 = inputs.p, fluxes.e, fluxes.qh
>>> test.dateformat = "%d.%m."
>>> inputs.p.series = (
... 0.0, 9.3, 3.2, 7.3, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 2.9, 0.2, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 3.3,
... 4.6, 0.8, 1.8, 1.1, 0.0, 5.0, 13.1, 14.6, 4.0, 0.8, 0.1, 3.3, 7.7, 10.3, 3.7,
... 15.3, 3.2, 2.7, 2.2, 8.0, 14.3, 6.3, 0.0, 5.9, 9.2, 6.1, 0.1, 0.0, 2.8, 10.6,
... 8.8, 7.2, 4.9, 1.8
... )
>>> model.petmodel.sequences.inputs.referenceevapotranspiration.series = (
... 0.3, 0.4, 0.4, 0.3, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2, 0.3, 0.3, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.3,
... 0.3, 0.2, 0.2, 0.3, 0.2, 0.2, 0.3, 0.6, 0.4, 0.4, 0.4, 0.5, 0.4, 0.3, 0.3, 0.5,
... 0.5, 0.3, 0.3, 0.4, 0.4, 0.3, 0.2, 0.1, 0.1, 0.0, 0.1, 0.1, 0.0, 0.2, 0.9, 0.9,
... 0.5, 0.9
... )
base example¶
The following parameter values do not agree with the ones of the
base example on application model gland_gr4 but with the ones of
the example given by Coron et al. (2023):
>>> imax(0.0)
>>> x1(242.257)
>>> x2(0.637)
>>> x3(53.517)
>>> x5(0.424)
>>> x6(4.759)
>>> with model.add_rconcmodel_directflow_v1("rconc_uh"):
... uh("gr_uh2", x4=2.218)
>>> with model.add_rconcmodel_routingstore_v1("rconc_uh"):
... uh("gr_uh1", x4=2.218)
>>> test.inits = (
... (states.i, 0.0),
... (states.s, 0.3 * x1),
... (states.r, 0.5 * x3),
... (states.r2, 0),
... (model.rconcmodel_routingstore.sequences.logs.quh, 0.0),
... (model.rconcmodel_directflow.sequences.logs.quh, 0.0),
... )
>>> conditions = test("gland_gr6_base_example", get_conditions="1990-01-01")
Click to see the table
Click to see the graphThere is no indication of an error in the water balance:
>>> from hydpy import round_
>>> round_(model.check_waterbalance(conditions))
0.0
groundwater loss¶
This integration test corresponds to the groundwater loss example on
gland_gr4:
>>> x2(-0.637)
>>> test.inits.s = 0.0
>>> test.inits.r = 0.0
>>> test.inits.r2 = 0.0
>>> conditions = test("gland_gr6_groundwater_loss", get_conditions="1990-01-01")
Click to see the table
Click to see the graphThere is no indication of an error in the water balance:
>>> round_(model.check_waterbalance(conditions))
0.0
interception¶
This integration test corresponds to the interception example on
gland_gr4:
>>> imax(10.0)
>>> x2(0.637)
>>> test.inits.s = 0.3 * x1
>>> test.inits.r = 0.5 * x3
>>> conditions = test("gland_gr6_interception", get_conditions="1990-01-01")
Click to see the table
Click to see the graphThere is no indication of an error in the water balance:
>>> round_(model.check_waterbalance(conditions))
0.0
no rconc submodels¶
This integration test corresponds to the no rconc submodels example on
gland_gr4:
>>> model.rconcmodel_directflow = None
>>> model.rconcmodel_routingstore = None
>>> conditions = test("gland_gr6_no_rconc_submodels", get_conditions="1990-01-01")
Click to see the table
Click to see the graphThere is no indication of an error in the water balance:
>>> round_(model.check_waterbalance(conditions))
0.0
- class hydpy.models.gland_gr6.Model[source]¶
Bases:
Main_PETModel_V1,Main_RConcModel_V2HydPy-G-GR6 (Génie Rural model with 6 parameters).
- The following “run methods” are called in the given sequence during each simulation step:
Calc_E_V1Let a submodel that conforms to thePETModel_V1interface calculate the potential evapotranspiration.Calc_EI_V1Calculate the actual evaporation from the interception store.Calc_PN_V1Calculate the net precipitation by considering all interception losses.Calc_EN_V1Calculate the net evapotranspiration capacity by considering interception evaporation.Update_I_V1Update the interception store based on precipitation, net precipitation, and interception evaporation.Calc_PS_V1Calculate the part of net precipitation filling the production store.Calc_ES_V1Calculate the actual evapotranspiration from the production store.Update_S_V1Update the production store by adding precipitation and evapotranspiration.Calc_Perc_V1Calculate the percolation from the production store.Update_S_V2Update the production store by subtracting percolation.Calc_AE_V1Calculate the total actual evapotranspiration.Calc_Pr_V1Calculate the total inflow into the runoff concentration module.Calc_PR1_PR9_V1SplitPRintoPR1andPR9.Calc_Q9_V1TransformPR9intoQ9.Calc_Q1_V1TransformPR1intoQ1.Calc_FR_V2Calculate the groundwater exchange affecting the routing store according to GR5 and GR6.Calc_FR2_V1Calculate the groundwater exchange affecting the exponential routing store.Update_R_V2Update the level of the non-linear routing store by adding its inflows according to GR6.Calc_QR_V1Calculate the outflow of the routing store.Update_R_V3Update the non-linear routing store by subtracting its outflow.Update_R2_V1Update the exponential routing store by adding its inflows.Calc_QR2_R2_V1Calculate the outflow of the exponential routing store and update its content.Calc_FD_V1Calculate the groundwater exchange affecting the direct runoff.Calc_QD_V1Calculate the direct runoff.Calc_QH_V2Calculate the total runoff according to GR6.Calc_QV_V1Calculate total discharge in m³/s.
- The following “outlet update methods” are called in the given sequence at the end of each simulation step:
Pass_Q_V1Update the outlet link sequence.
- The following “additional methods” might be called by one or more of the other methods or are meant to be directly called by the user:
Calc_E_PETModel_V1Let a submodel that conforms to thePETModel_V1interface calculate the potential evapotranspiration.Calc_Q_RConcModel_V1Let a submodel that follows theRConcModel_V1submodel interface perform runoff concentration.Calc_Q_RConcModel_V1Let a submodel that follows theRConcModel_V1submodel interface perform runoff concentration.
- Users can hook submodels into the defined main model if they satisfy one of the following interfaces:
PETModel_V1Simple interface for calculating all potential evapotranspiration values in one step.RConcModel_V1Simple interface for calculating runoff concentration processes.
- DOCNAME = ('G-GR6', 'Génie Rural model with 6 parameters')¶
- petmodel¶
Required submodel that complies with the following interface: PETModel_V1.
- rconcmodel_routingstore¶
Optional submodel that complies with the following interface: RConcModel_V1.
- rconcmodel_directflow¶
Optional submodel that complies with the following interface: RConcModel_V1.
- check_waterbalance(initial_conditions: dict[str, dict[str, dict[str, float | ndarray[tuple[Any, ...], dtype[float64]]]]]) float[source]¶
Determine the water balance error of the previous simulation run in mm.
Method
check_waterbalance()calculates the balance error as follows:\[\begin{split}Error = \Sigma InOut - \Delta Vol - \Delta Rconc \\ \\ \Sigma InOut = \sum_{t=t0}^{t1} P_t - AE_t + FR_t + FR2_t + FD_t - QH_t \\ \Delta Vol = \left( I_{t1} - I_{t0} \right) + \left( S_{t1} - S_{t0} \right) + \left( R_{t1} - R_{t0} \right) \\ \Delta Rconc = get\_waterbalance_{direct \ flow}(*) + get\_waterbalance_{routing \ store}(*)\end{split}\]
- REUSABLE_METHODS = ()¶
- class hydpy.models.gland_gr6.ControlParameters(master: Parameters, cls_fastaccess: type[FastAccessParameter] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
SubParametersControl parameters of model gland_gr6.
- The following classes are selected:
Area()Subbasin area [km²].IMax()Interception store capacity [mm].X1()Maximum capacity of the production storage [mm].X2()Groundwater exchange coefficient (positive for water imports, negative for exports) [mm/T].X3()One timestep ahead maximum capacity of the routing store [mm].X5()Intercatchment exchange threshold [-].X6()Coefficient for emptying the exponential store [mm].
- class hydpy.models.gland_gr6.DerivedParameters(master: Parameters, cls_fastaccess: type[FastAccessParameter] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
SubParametersDerived parameters of model gland_gr6.
- class hydpy.models.gland_gr6.FluxSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
FluxSequencesFlux sequences of model gland_gr6.
- The following classes are selected:
E()Potential evapotranspiration [mm/T].EN()Net evapotranspiration capacity [mm/T].PN()Net precipitation [mm/T].EI()Actual evaporation from the interception store [mm/T].ES()Actual evapotranspiration from the production store [mm/T].AE()Total actual evapotranspiration [mm/T].PR()Total inflow into the runoff concentration module [mm/T].Perc()Percolation [mm/T].Q9()Outflow of runoff concentration submodel receivingPR9[mm/T].Q1()Outflow of runoff concentration submodel receivingPR1[mm/T].FD()Groundwater exchange affecting the direct runoff [mm/T].FR()Groundwater exchange affecting the routing store [mm/T].FR2()Groundwater exchange affecting the exponential routing store [mm/T].QR()Outflow of the routing store [mm/T].QR2()Outflow of the exponential store [mm/T].QD()Direct runoff [mm/T].QH()Total runoff [mm/T].QV()Total discharge [m³/s].
- class hydpy.models.gland_gr6.InputSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
InputSequencesInput sequences of model gland_gr6.
- The following classes are selected:
P()Precipitation [mm/T].
- class hydpy.models.gland_gr6.OutletSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
OutletSequencesOutlet sequences of model gland_gr6.
- The following classes are selected:
Q()Runoff [m³/s].
- class hydpy.models.gland_gr6.StateSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
StateSequencesState sequences of model gland_gr6.
