HydPy-KinW (base model)¶
The HydPy-KinW model family provides features for implementing storage based routing methods similar to those implemented by the water balance model LARSIM.
Method Features¶
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Model[source]¶
Bases:
ELSModel,SegmentModelHydPy-KinW (base model).
- The following “inlet update methods” are called in the given sequence at the beginning of each simulation step:
Pick_Q_V1Query the current inflow from all inlet nodes.Pick_Inflow_V1Sum up the current inflow from all inlet nodes.
- The following methods define the relevant components of a system of ODE equations (e.g. direct runoff):
Calc_RHM_V1Regularise the stage with respect to the channel bottom.Calc_RHMDH_V1Calculate the derivative of the stage regularised with respect to the channel bottom.Calc_RHV_V1Regularise the stage with respect to the transition from the main channel to both forelands.Calc_RHVDH_V1Calculate the derivative of the stage regularised with respect to the transition from the main channel to both forelands.Calc_RHLVR_RHRVR_V1Regularise the stage with respect to the transitions from the forelands to the outer embankments.Calc_RHLVRDH_RHRVRDH_V1Calculate the derivative of the stage regularised with respect to the transition from the forelands to the outer embankments.Calc_AM_UM_V1Calculate the wetted area and the wetted perimeter of the main channel.Calc_AMDH_UMDH_V1Calculate the derivatives of the wetted area and perimeter of the main channel.Calc_ALV_ARV_ULV_URV_V1Calculate the wetted area and wetted perimeter of both forelands.Calc_ALVDH_ARVDH_ULVDH_URVDH_V1Calculate the derivatives of the wetted area and perimeter of both forelands.Calc_ALVR_ARVR_ULVR_URVR_V1Calculate the wetted area and perimeter of both outer embankments.Calc_ALVRDH_ARVRDH_ULVRDH_URVRDH_V1Calculate the derivatives of the wetted area and perimeter of both outer embankments.Calc_QM_V1Calculate the discharge of the main channel after Manning-Strickler.Calc_QMDH_V1Calculate the derivative of the discharge of the main channel following methodCalc_QM_V1.Calc_QM_V2Calculate the discharge of the main channel following the kinematic wave approach.Calc_QLV_QRV_V1Calculate the discharge of both forelands after Manning-Strickler.Calc_QLVDH_QRVDH_V1Calculate the derivative of both forelands’ discharge with respect to the stage following methodCalc_QLV_QRV_V1.Calc_QLV_QRV_V2Calculate the discharge of both forelands following the kinematic wave approach.Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V1Calculate the discharge of both outer embankments after Manning-Strickler.Calc_QLVRDH_QRVRDH_V1Calculate the derivative of the discharge over the outer embankments with respect to the stage following methodCalc_QLVR_QRVR_V1.Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V2Calculate the discharge of both outer embankments following the kinematic wave approach.Calc_AG_V1Calculate the through wetted of the total cross-sections.Calc_QG_V1Calculate the discharge of the total cross-section.Calc_QG_V2Calculate the discharge of the total cross-section based on an interpolated flow velocity.Calc_QA_V1Query the actual outflow.Calc_WBM_V1Calculate the water table width above the main channel.Calc_WBLV_WBRV_V1Calculate the water table width above both forelands.Calc_WBLVR_WBRVR_V1Calculate the water table width above both outer embankments.Calc_WBG_V1Calculate the water level width of the total cross-section.Calc_DH_V1Determine the change in the stage.
- The following methods define the complete equations of an ODE system (e.g. change in storage of fast water due to effective precipitation and direct runoff):
Update_H_V1Update the stage.Update_VG_V1Update the water volume.
- The following “outlet update methods” are called in the given sequence at the end of each simulation step:
Pass_Q_V1Pass the outflow to the outlet node.Calc_Outflow_V1Take the inflow as the outflow for channels zero-segment channels.Pass_Outflow_V1Pass the outflow to the outlet node.
- The following “additional methods” might be called by one or more of the other methods or are meant to be directly called by the user:
Return_QF_V1Calculate and return the “error” between the actual discharge and the discharge corresponding to the given water stage.Return_H_V1Calculate and return the water stage corresponding to the current discharge value.Update_WaterVolume_V1Update the old water volume with the current inflow.Return_InitialWaterVolume_V1Calculate and return the initial water volume that agrees with the given final water depth following the implicit Euler method.Return_VolumeError_V1Calculate and return the difference between the initial water volume that stems from the last simulation step plus the current inflow and the water volume that agrees with the given final water depth following the implicit Euler method.Calc_WaterDepth_V1Determine the new water depth based on the implicit Euler method.Update_WaterVolume_V2Calculate the new water volume that agrees with the previously calculated final water depth.Calc_InternalFlow_Outflow_V1Calculate the flow out of the channel segments.
- The following “submodels” might be called by one or more of the implemented methods or are meant to be directly called by the user:
PegasusHPegasus iterator for finding the correct water stage.PegasusImplicitEulerPegasus iterator for determining the water level at the end of a simulation step.
- DOCNAME = ('KinW', 'base model')¶
- wqmodel¶
Required submodel that complies with the following interface: CrossSectionModel_V1.
- wqmodel_is_mainmodel¶
- wqmodel_typeid¶
- REUSABLE_METHODS = ()¶
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Pick_Q_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodQuery the current inflow from all inlet nodes.
- Basic equation:
\(QZ = \sum Q\)
Example:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> inlets.q.shape = 2 >>> inlets.q = 2.0, 4.0 >>> model.pick_q_v1() >>> fluxes.qz qz(6.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Pick_Inflow_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodSum up the current inflow from all inlet nodes.
- Basic equation:
\(Inflow = \sum Q\)
Example:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> inlets.q.shape = 2 >>> inlets.q = 2.0, 4.0 >>> model.pick_inflow_v1() >>> fluxes.inflow inflow(6.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_QZA_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the current inflow into the channel.
- Basic equation:
\(QZA = QZ\)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_RHM_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodRegularise the stage with respect to the channel bottom.
- Required by the method:
- Requires the control parameter:
- Requires the derived parameter:
- Requires the state sequence:
- Calculates the aide sequence:
- Used auxiliary method:
smooth_logistic2()- Basic equation:
\(RHM = smooth_{logistic2}(H, HRP)\)
Examples:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(5) >>> states.h = -1.0, -0.1, 0.0, 0.1, 1.0
>>> hr(0.0) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> aides.rhm rhm(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.1, 1.0)
>>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> aides.rhm rhm(0.0, 0.01, 0.040983, 0.11, 1.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_RHMDH_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the derivative of the stage regularised with respect to the channel bottom.
- Required by the method:
- Requires the control parameter:
- Requires the derived parameter:
- Requires the state sequence:
- Calculates the aide sequence:
- Used auxiliary method:
smooth_logistic2_derivative2()- Basic equation:
\(RHMDH = smooth_{logistic2'}(H, HRP)\)
Examples:
We apply the class
NumericalDifferentiatorto validate the calculated derivatives:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(5) >>> states.h = -1.0, -0.1, 0.0, 0.1, 1.0
>>> hr(0.0) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> model.calc_rhmdh_v1() >>> aides.rhmdh rhmdh(0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
>>> from hydpy import NumericalDifferentiator >>> numdiff = NumericalDifferentiator( ... xsequence=states.h, ... ysequences=[aides.rhm], ... methods=[model.calc_rhm_v1]) >>> numdiff() d_rhm/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0
>>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> model.calc_rhmdh_v1() >>> aides.rhmdh rhmdh(0.0, 0.155602, 0.5, 0.844398, 1.0)
>>> numdiff() d_rhm/d_h: 0.0, 0.155602, 0.5, 0.844398, 1.0
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_RHV_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodRegularise the stage with respect to the transition from the main channel to both forelands.
- Used auxiliary method:
smooth_logistic2()- Basic equation:
\(RHV = smooth_{logistic2}(H-HM, HRP)\)
Examples:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(5) >>> hm(1.0) >>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> states.h = 0.0, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1, 2.0 >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> aides.rhv rhv(0.0, 0.01, 0.040983, 0.11, 1.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_RHVDH_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the derivative of the stage regularised with respect to the transition from the main channel to both forelands.
- Used auxiliary method:
smooth_logistic2_derivative2()- Basic equation:
\(RHVDH = smooth_{logistic2'}(H-HM, HRP)\)
Examples:
We apply the class
NumericalDifferentiatorto validate the calculated derivatives:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(5) >>> hm(1.0) >>> states.h = 0.0, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1, 2.0
>>> hr(0.0) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> aides.rhvdh rhvdh(0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
>>> from hydpy import NumericalDifferentiator >>> numdiff = NumericalDifferentiator( ... xsequence=states.h, ... ysequences=[aides.rhv], ... methods=[model.calc_rhv_v1]) >>> numdiff() d_rhv/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0
>>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> aides.rhvdh rhvdh(0.0, 0.155602, 0.5, 0.844398, 1.0)
>>> numdiff() d_rhv/d_h: 0.0, 0.155602, 0.5, 0.844398, 1.0
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_RHLVR_RHRVR_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodRegularise the stage with respect to the transitions from the forelands to the outer embankments.
- Used auxiliary method:
smooth_logistic2()- Basic equation:
\(RHVR = smooth_{logistic2}(H-HM-HV, HRP)\)
Examples:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(6) >>> hm(1.0) >>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=1.1) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> states.h = 1.0, 1.9, 2.0, 2.1, 2.2, 3.0 >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> aides.rhlvr rhlvr(0.0, 0.01, 0.040983, 0.11, 0.201974, 1.0) >>> aides.rhrvr rhrvr(0.0, 0.001974, 0.01, 0.040983, 0.11, 0.9)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_RHLVRDH_RHRVRDH_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the derivative of the stage regularised with respect to the transition from the forelands to the outer embankments.
- Used auxiliary method:
smooth_logistic2_derivative2()- Basic equation:
\(RHVDH = smooth_{logistic2'}(H-HM-HV, HRP)\)
Examples:
We apply the class
NumericalDifferentiatorto validate the calculated derivatives:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(8) >>> hm(1.0) >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=2.0) >>> states.h = 1.0, 1.9, 2.0, 2.1, 2.9, 3.0, 3.1, 4.0
>>> hr(0.0) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> aides.rhlvrdh rhlvrdh(0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0) >>> aides.rhrvrdh rhrvrdh(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
>>> from hydpy import NumericalDifferentiator >>> numdiff = NumericalDifferentiator( ... xsequence=states.h, ... ysequences=[aides.rhlvr, aides.rhrvr], ... methods=[model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1]) >>> numdiff() d_rhlvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 d_rhrvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0
>>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> aides.rhlvrdh rhlvrdh(0.0, 0.155602, 0.5, 0.844398, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0) >>> aides.rhrvrdh rhrvrdh(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.155602, 0.5, 0.844398, 1.0)
>>> numdiff() d_rhlvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.155602, 0.5, 0.844398, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 d_rhrvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.155602, 0.5, 0.844398, 1.0
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_AM_UM_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the wetted area and the wetted perimeter of the main channel.
The main channel is assumed to have identical slopes on both sides. Water flowing exactly above the main channel contributes to
AM. Both theoretical surfaces separating the water above the main channel from the water above the forelands contribute toUM.Examples:
Generally, a trapezoid with reflection symmetry is assumed. Here, we set its smaller base (bottom) to a length of 2 meters, its legs to an inclination of 1 meter per 4 meters, and its height (depths) to 1 meter:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(8) >>> bm(2.0) >>> bnm(4.0) >>> derived.bnmf.update()
First, we show that all calculations agree with the unmodified triple trapezoid profile results when setting the smoothing parameter
HRPto zero:>>> derived.hrp(0)
This example deals with normal flow conditions, where water flows within the main channel completely (
H<HM, the first five channel sections), and with high flow conditions, where water flows over the foreland also (H>HM, the three last channel sections):>>> hm(1.0) >>> states.h = 0.0, 0.1, 0.5, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1, 1.5, 2.0 >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_am_um_v1() >>> aides.am am(0.0, 0.24, 2.0, 5.04, 6.0, 7.0, 11.0, 16.0) >>> aides.um um(2.0, 2.824621, 6.123106, 9.42159, 10.246211, 10.446211, 11.246211, 12.246211)
The next example checks the special case of a channel with zero height:
>>> hm(0.0) >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_am_um_v1() >>> aides.am am(0.0, 0.2, 1.0, 1.8, 2.0, 2.2, 3.0, 4.0) >>> aides.um um(2.0, 2.2, 3.0, 3.8, 4.0, 4.2, 5.0, 6.0)
Second, we repeat both examples with a reasonable smoothing parameterisation. The primary deviations occur around the original discontinuities related to the channel bottom and the main channel’s transition to both forelands:
>>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hrp.update()
>>> hm(1.0) >>> states.h = 0.0, 0.1, 0.5, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1, 1.5, 2.0 >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_am_um_v1() >>> aides.am am(0.088684, 0.2684, 2.000075, 5.0396, 5.993282, 6.9916, 10.99995, 16.0) >>> aides.um um(2.337952, 2.907083, 6.123131, 9.359128, 9.990225, 10.383749, 11.246133, 12.246211)
>>> hm(0.0) >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_am_um_v1() >>> aides.am am(0.081965, 0.22, 1.000025, 1.8, 2.0, 2.2, 3.0, 4.0) >>> aides.um um(2.081965, 2.22, 3.000025, 3.8, 4.0, 4.2, 5.0, 6.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_AMDH_UMDH_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the derivatives of the wetted area and perimeter of the main channel.
Examples:
In the following, we repeat the examples of the documentation on method
Calc_AM_UM_V1and check the derivatives’ correctness by comparing the results of classNumericalDifferentiator:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(8) >>> bm(2.0) >>> bnm(4.0)
>>> derived.bnmf.update() >>> derived.hrp(0)
>>> hm(1.0) >>> states.h = 0.0, 0.1, 0.5, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1, 1.5, 2.0 >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> model.calc_rhmdh_v1() >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> model.calc_amdh_umdh_v1() >>> aides.amdh amdh(2.0, 2.8, 6.0, 9.2, 10.0, 10.0, 10.0, 10.0) >>> aides.umdh umdh(8.246211, 8.246211, 8.246211, 8.246211, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0)
>>> from hydpy import NumericalDifferentiator >>> numdiff = NumericalDifferentiator( ... xsequence=states.h, ... ysequences=[aides.am, aides.um], ... methods=[model.calc_rhm_v1, ... model.calc_rhv_v1, ... model.calc_am_um_v1]) >>> numdiff() d_am/d_h: 2.0, 2.8, 6.0, 9.2, 10.0, 10.0, 10.0, 10.0 d_um/d_h: 8.246211, 8.246211, 8.246211, 8.246211, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0
>>> hm(0.0) >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> model.calc_rhmdh_v1() >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> model.calc_amdh_umdh_v1() >>> aides.amdh amdh(2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0) >>> aides.umdh umdh(2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0) >>> numdiff() d_am/d_h: 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0 d_um/d_h: 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0
>>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hrp.update()
>>> hm(1.0) >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> model.calc_rhmdh_v1() >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> model.calc_amdh_umdh_v1() >>> aides.amdh amdh(1.163931, 2.431865, 5.998826, 9.18755, 9.836069, 10.05693, 10.000749, 10.0) >>> aides.umdh umdh(4.123105, 6.963079, 8.243132, 7.274283, 5.123105, 2.971926, 2.001327, 2.0)
>>> numdiff() d_am/d_h: 1.163931, 2.431865, 5.998826, 9.18755, 9.836069, 10.05693, 10.000749, 10.0 d_um/d_h: 4.123105, 6.963079, 8.243132, 7.274283, 5.123105, 2.971926, 2.001327, 2.0
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_ALV_ARV_ULV_URV_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the wetted area and wetted perimeter of both forelands.
Each foreland lies between the main channel and one outer embankment. The water flowing exactly above a foreland is contributing to
ALVorARV. The theoretical surface separating the water above the main channel from the water above the foreland is not contributing toULVorURV. On the other hand, the surface separating the water above the foreland from the water above its outer embankment is contributing toULVandURV.Examples:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(14) >>> hm(1.0)
First, we show that all calculations agree with the unmodified triple trapezoid profile results when setting the smoothing parameter
HRPto zero:>>> derived.hrp(0)
This example deals with normal flow conditions, where water flows within the main channel completely (
H<HM, the first four channel sections); with moderate high flow conditions, where water flows over both forelands, but not over their embankments (HM<H< (HM+HV), channel sections six to eight or twelve for the left and the right foreland, respectively), and with extreme high flow conditions, where water flows over both forelands and their outer embankments ((HM+HV) <H, the last six or two channel sections for the left and the right foreland, respectively):>>> bv(left=2.0, right=3.0) >>> bnv(left=4.0, right=5.0) >>> derived.bnvf.update() >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=2.0)
>>> states.h = (0.0, 0.5, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1, 1.5, 1.9, ... 2.0, 2.1, 2.5, 2.9, 3.0, 3.1, 4.0) >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_alv_arv_ulv_urv_v1() >>> aides.alv alv(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.22, 1.5, 3.42, 4.0, 4.6, 7.0, 9.4, 10.0, 10.6, 16.0) >>> aides.arv arv(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.325, 2.125, 4.725, 5.5, 6.325, 10.125, 14.725, 16.0, 17.3, 29.0) >>> aides.ulv ulv(2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.412311, 4.061553, 5.710795, 6.123106, 6.223106, 6.623106, 7.023106, 7.123106, 7.223106, 8.123106) >>> aides.urv urv(3.0, 3.0, 3.0, 3.0, 3.509902, 5.54951, 7.589118, 8.09902, 8.608921, 10.648529, 12.688137, 13.198039, 13.298039, 14.198039)
The next example proves the correct handling of forelands with zero widths and heights:
>>> bv(left=0.0, right=2.0) >>> bnv(4.0) >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=0.0) >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_alv_arv_ulv_urv_v1() >>> aides.alv alv(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.02, 0.5, 1.62, 2.0, 2.4, 4.0, 5.6, 6.0, 6.4, 10.0) >>> aides.arv arv(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.2, 1.0, 1.8, 2.0, 2.2, 3.0, 3.8, 4.0, 4.2, 6.0) >>> aides.ulv ulv(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.412311, 2.061553, 3.710795, 4.123106, 4.223106, 4.623106, 5.023106, 5.123106, 5.223106, 6.123106) >>> aides.urv urv(2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.1, 2.5, 2.9, 3.0, 3.1, 3.5, 3.9, 4.0, 4.1, 5.0)
Second, we repeat both examples with a reasonable smoothing parameterisation. The primary deviations occur around the original discontinuities related to the channel bottom and the main channel’s transition to both forelands:
>>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hrp.update()
>>> bv(left=2.0, right=3.0) >>> bnv(left=4.0, right=5.0) >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=2.0) >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_alv_arv_ulv_urv_v1() >>> aides.alv alv(0.0, 0.000025, 0.0202, 0.085324, 0.2442, 1.50005, 3.4198, 3.996641, 4.5958, 6.999975, 9.4, 10.0, 10.6, 16.0) >>> aides.arv arv(0.0, 0.000038, 0.03025, 0.127147, 0.36025, 2.125069, 4.725, 5.5, 6.325, 10.125, 14.72475, 15.995801, 17.29475, 29.0) >>> aides.ulv ulv(2.0, 2.000052, 2.041231, 2.168976, 2.453542, 4.061565, 5.679564, 5.995113, 6.191875, 6.623066, 7.023106, 7.123106, 7.223106, 8.123106) >>> aides.urv urv(3.0, 3.000064, 3.05099, 3.208971, 3.560892, 5.549574, 7.589118, 8.09902, 8.608921, 10.648478, 12.647147, 13.03005, 13.257049, 14.198039)
>>> bv(left=0.0, right=2.0) >>> bnv(4.0) >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=0.0) >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_alv_arv_ulv_urv_v1() >>> aides.alv alv(0.0, 0.0, 0.0002, 0.003359, 0.0242, 0.500025, 1.6198, 1.996641, 2.3958, 3.999975, 5.6, 6.0, 6.4, 10.0) >>> aides.arv arv(0.0, 0.000025, 0.02, 0.081965, 0.22, 1.000025, 1.8, 2.0, 2.2, 3.0, 3.8, 4.0, 4.2, 6.0) >>> aides.ulv ulv(0.0, 0.000052, 0.041231, 0.168976, 0.453542, 2.061565, 3.679564, 3.995113, 4.191875, 4.623066, 5.023106, 5.123106, 5.223106, 6.123106) >>> aides.urv urv(2.0, 2.000013, 2.01, 2.040983, 2.11, 2.500013, 2.9, 3.0, 3.1, 3.5, 3.9, 4.0, 4.1, 5.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_ALVDH_ARVDH_ULVDH_URVDH_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the derivatives of the wetted area and perimeter of both forelands.
Examples:
In the following, we repeat the examples of the documentation on method
Calc_ALV_ARV_ULV_URV_V1and check the derivatives’ correctness by comparing the results of classNumericalDifferentiator:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(13) >>> hm(1.0) >>> bv(left=2.0, right=3.0) >>> bnv(left=4.0, right=5.0) >>> derived.bnvf.update() >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=2.0)
>>> derived.hrp(0)
>>> states.h = (1.0, 1.5, 1.9, 2.0, 2.1, 2.5, 3.0, ... 3.5, 3.9, 4.0, 4.1, 4.5, 5.0) >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> model.calc_alvdh_arvdh_ulvdh_urvdh_v1() >>> aides.alvdh alvdh(2.0, 4.0, 5.6, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0) >>> aides.arvdh arvdh(3.0, 5.5, 7.5, 8.0, 8.5, 10.5, 13.0, 13.0, 13.0, 13.0, 13.0, 13.0, 13.0) >>> aides.ulvdh ulvdh(4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0) >>> aides.urvdh urvdh(5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
>>> from hydpy import NumericalDifferentiator >>> numdiff = NumericalDifferentiator( ... xsequence=states.h, ... ysequences=[aides.alv, aides.arv, aides.ulv, aides.urv], ... methods=[model.calc_rhv_v1, ... model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1, ... model.calc_alv_arv_ulv_urv_v1]) >>> numdiff() d_alv/d_h: 2.0, 4.0, 5.6, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0 d_arv/d_h: 3.0, 5.5, 7.5, 8.0, 8.5, 10.5, 13.0, 13.0, 13.0, 13.0, 13.0, 13.0, 13.0 d_ulv/d_h: 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 d_urv/d_h: 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0
>>> bv(left=0.0, right=2.0) >>> bnv(4.0) >>> derived.bnvf.update() >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=0.0) >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> model.calc_alvdh_arvdh_ulvdh_urvdh_v1() >>> aides.alvdh alvdh(0.0, 2.0, 3.6, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0) >>> aides.arvdh arvdh(2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0) >>> aides.ulvdh ulvdh(4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0) >>> aides.urvdh urvdh(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0) >>> numdiff() d_alv/d_h: 0.0, 2.0, 3.6, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0, 4.0 d_arv/d_h: 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0 d_ulv/d_h: 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 d_urv/d_h: 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0
>>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hrp.update()
>>> bv(left=2.0, right=3.0) >>> bnv(left=4.0, right=5.0) >>> derived.bnvf.update() >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=2.0)
>>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> model.calc_alvdh_arvdh_ulvdh_urvdh_v1() >>> aides.alvdh alvdh(1.081965, 3.9992, 5.593775, 5.918034, 6.028465, 6.000375, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0) >>> aides.arvdh arvdh(1.602457, 5.498894, 7.499998, 8.0, 8.5, 10.5, 12.897543, 13.000468, 13.000001, 13.0, 13.0, 13.0, 13.0) >>> aides.ulvdh ulvdh(2.061553, 4.121566, 3.637142, 2.561553, 1.485963, 1.000664, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0) >>> aides.urvdh urvdh(2.54951, 5.097936, 5.099018, 5.099019, 5.099018, 5.098149, 3.04951, 1.000871, 1.000001, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
>>> numdiff() d_alv/d_h: 1.081965, 3.9992, 5.593775, 5.918034, 6.028465, 6.000375, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0, 6.0 d_arv/d_h: 1.602457, 5.498894, 7.499998, 8.0, 8.5, 10.5, 12.897543, 13.000468, 13.000001, 13.0, 13.0, 13.0, 13.0 d_ulv/d_h: 2.061553, 4.121566, 3.637142, 2.561553, 1.485963, 1.000664, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 d_urv/d_h: 2.54951, 5.097936, 5.099018, 5.099019, 5.099018, 5.098149, 3.04951, 1.000871, 1.000001, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_ALVR_ARVR_ULVR_URVR_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the wetted area and perimeter of both outer embankments.
Each outer embankment lies beyond its foreland. The water flowing exactly above an embankment adds to
ALVRandARVR. The theoretical surface separating water above the foreland from the water above its embankment is not contributing toULVRandURVR.Examples:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(11) >>> hm(1.0)
First, we show that all calculations agree with the unmodified triple trapezoid profile results when the setting the smoothing parameter
HRPto zero:>>> derived.hrp(0)
This example deals with moderate high flow conditions, where water flows over the forelands, but not over their outer embankments (
HM<H< (HM+HV), the first four or eight channel sections for the left and the right outer embankment, respectively); the second example deals with extreme high flow conditions, where water flows both over the foreland and their outer embankments ((HM+HV) <H, the last seven or three channel sections for the left and the right outer embankment, respectively):>>> states.h = 1.0, 1.5, 1.9, 2.0, 2.1, 2.5, 2.9, 3.0, 3.1, 3.5, 4.0 >>> bnvr(left=4.0, right=5.0) >>> derived.bnvrf.update() >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=2.0) >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_alvr_arvr_ulvr_urvr_v1() >>> aides.alvr alvr(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.02, 0.5, 1.62, 2.0, 2.42, 4.5, 8.0) >>> aides.arvr arvr(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.025, 0.625, 2.5) >>> aides.ulvr ulvr(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.412311, 2.061553, 3.710795, 4.123106, 4.535416, 6.184658, 8.246211) >>> aides.urvr urvr(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.509902, 2.54951, 5.09902)
The next example checks the special cases of a vertical outer embankment (left side) and zero-height foreland (right side):
>>> bnvr(left=0.0, right=5.0) >>> derived.bnvrf.update() >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=0.0) >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_alvr_arvr_ulvr_urvr_v1() >>> aides.alvr alvr(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0) >>> aides.arvr arvr(0.0, 0.625, 2.025, 2.5, 3.025, 5.625, 9.025, 10.0, 11.025, 15.625, 22.5) >>> aides.ulvr ulvr(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.1, 0.5, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1, 1.5, 2.0) >>> aides.urvr urvr(0.0, 2.54951, 4.589118, 5.09902, 5.608921, 7.648529, 9.688137, 10.198039, 10.707941, 12.747549, 15.297059)
Second, we repeat both examples with a reasonable smoothing parameterisation. The primary deviations occur around the original discontinuities related to the channel bottom and the main channel’s transition to both forelands:
>>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> bnvr(left=4.0, right=5.0) >>> derived.bnvrf.update() >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=2.0) >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_alvr_arvr_ulvr_urvr_v1() >>> aides.alvr alvr(0.0, 0.0, 0.0002, 0.003359, 0.0242, 0.500025, 1.62, 2.0, 2.42, 4.5, 8.0) >>> aides.arvr arvr(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.00025, 0.004199, 0.03025, 0.625031, 2.5) >>> aides.ulvr ulvr(0.0, 0.000052, 0.041231, 0.168976, 0.453542, 2.061605, 3.710795, 4.123106, 4.535416, 6.184658, 8.246211) >>> aides.urvr urvr(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.000064, 0.05099, 0.208971, 0.560892, 2.549574, 5.09902)
>>> bnvr(left=0.0, right=5.0) >>> derived.bnvrf.update() >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=0.0) >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_alvr_arvr_ulvr_urvr_v1() >>> aides.alvr alvr(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0) >>> aides.arvr arvr(0.004199, 0.625031, 2.025, 2.5, 3.025, 5.625, 9.025, 10.0, 11.025, 15.625, 22.5) >>> aides.ulvr ulvr(0.0, 0.000013, 0.01, 0.040983, 0.11, 0.500013, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1, 1.5, 2.0) >>> aides.urvr urvr(0.208971, 2.549574, 4.589118, 5.09902, 5.608921, 7.648529, 9.688137, 10.198039, 10.707941, 12.747549, 15.297059)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_ALVRDH_ARVRDH_ULVRDH_URVRDH_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the derivatives of the wetted area and perimeter of both outer embankments.
Examples:
In the following, we repeat the examples of the documentation on method
Calc_ALVR_ARVR_ULVR_URVR_V1and check the derivatives’ correctness by comparing the results of classNumericalDifferentiator:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(11) >>> hm(1.0)
>>> derived.hrp(0)
>>> states.h = 1.0, 1.5, 1.9, 2.0, 2.1, 2.5, 2.9, 3.0, 3.1, 3.5, 4.0 >>> bnvr(left=4.0, right=5.0) >>> derived.bnvrf.update() >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=2.0) >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> model.calc_alvrdh_arvrdh_ulvrdh_urvrdh_v1() >>> aides.alvrdh alvrdh(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.4, 2.0, 3.6, 4.0, 4.4, 6.0, 8.0) >>> aides.arvrdh arvrdh(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 2.5, 5.0) >>> aides.ulvrdh ulvrdh(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106) >>> aides.urvrdh urvrdh(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902)
>>> from hydpy import NumericalDifferentiator >>> numdiff = NumericalDifferentiator( ... xsequence=states.h, ... ysequences=[aides.alvr, aides.arvr, aides.ulvr, aides.urvr], ... methods=[model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1, ... model.calc_alvr_arvr_ulvr_urvr_v1]) >>> numdiff() d_alvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.4, 2.0, 3.6, 4.0, 4.4, 6.0, 8.0 d_arvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 2.5, 5.0 d_ulvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106 d_urvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902
>>> bnvr(left=0.0, right=5.0) >>> derived.bnvrf.update() >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=0.0) >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> model.calc_alvrdh_arvrdh_ulvrdh_urvrdh_v1() >>> aides.alvrdh alvrdh(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0) >>> aides.arvrdh arvrdh(0.0, 2.5, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5, 7.5, 9.5, 10.0, 10.5, 12.5, 15.0) >>> aides.ulvrdh ulvrdh(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0) >>> aides.urvrdh urvrdh(5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902)
>>> numdiff() d_alvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 d_arvr/d_h: 0.0, 2.5, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5, 7.5, 9.5, 10.0, 10.5, 12.5, 15.0 d_ulvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 d_urvr/d_h: 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902, 5.09902
>>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> bnvr(left=4.0, right=5.0) >>> derived.bnvrf.update() >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=2.0) >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> model.calc_alvrdh_arvrdh_ulvrdh_urvrdh_v1() >>> aides.alvrdh alvrdh(0.0, 0.0, 0.006224, 0.081965, 0.371535, 1.999625, 3.599999, 4.0, 4.4, 6.0, 8.0) >>> aides.arvrdh arvrdh(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.00778, 0.102457, 0.464419, 2.499532, 5.0) >>> aides.ulvrdh ulvrdh(0.0, 0.000876, 0.641565, 2.061553, 3.48154, 4.12223, 4.123105, 4.123105, 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106) >>> aides.urvrdh urvrdh(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.000001, 0.001083, 0.79342, 2.54951, 4.305599, 5.097936, 5.099019)
>>> numdiff() d_alvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.006224, 0.081965, 0.371535, 1.999625, 3.599999, 4.0, 4.4, 6.0, 8.0 d_arvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.00778, 0.102457, 0.464419, 2.499532, 5.0 d_ulvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.000876, 0.641565, 2.061553, 3.48154, 4.12223, 4.123105, 4.123105, 4.123106, 4.123106, 4.123106 d_urvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.000001, 0.001083, 0.79342, 2.54951, 4.305599, 5.097936, 5.099019
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_QM_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the discharge of the main channel after Manning-Strickler.
- Basic equation:
\(QM = MFM \cdot \frac{AM^{5/3}}{UM^{2/3}}\)
Examples:
Note the handling of zero values for
UM(in the third subsection):>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(3) >>> derived.mfm(10.0) >>> aides.am = 3.0, 0.0, 3.0 >>> aides.um = 7.0, 7.0, 0.0 >>> model.calc_qm_v1() >>> aides.qm qm(17.053102, 0.0, 0.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_QM_V2[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the discharge of the main channel following the kinematic wave approach.
- Basic equation:
\(QM = \frac{QMDH}{AMDH} \cdot AM\)
Examples:
Note the handling of zero values for
AMDH(in the second subsection):>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(2) >>> aides.am = 4.0, 4.0 >>> aides.qmdh = 3.0, 3.0 >>> aides.amdh = 2.0, 0.0 >>> model.calc_qm_v2() >>> aides.qm qm(6.0, 0.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_QMDH_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the derivative of the discharge of the main channel following method
Calc_QM_V1.- Basic equation:
\(QMDH = MFM \cdot \frac{5 \cdot AM^{2/3} \cdot AMDH}{3 \cdot UM^{2/3}} - \frac{2 \cdot AM^{5/3} \cdot UMDH}{3 \cdot UM^{5/3}}\)
Examples:
First, we apply the class
NumericalDifferentiatorto validate the calculated derivatives:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(2) >>> bm(2.0) >>> bnm(4.0) >>> hm(2.0) >>> derived.mfm(10.0) >>> derived.hrp(0.0) >>> derived.bnmf.update() >>> states.h = 0.0, 1.0 >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> model.calc_rhmdh_v1() >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> model.calc_am_um_v1() >>> model.calc_amdh_umdh_v1() >>> model.calc_qmdh_v1() >>> aides.qmdh qmdh(0.0, 94.12356)
>>> from hydpy import NumericalDifferentiator,pub >>> numdiff = NumericalDifferentiator( ... xsequence=states.h, ... ysequences=[aides.qm], ... methods=[model.calc_rhm_v1, ... model.calc_rhv_v1, ... model.calc_am_um_v1, ... model.calc_qm_v1], ... dx=1e-8) >>> with pub.options.reprdigits(5): ... numdiff() d_qm/d_h: 0.00002, 94.12356
Second, we show that zero values for
AMorUMresult in zero values forQMDH:>>> aides.am = 1.0, 0.0 >>> aides.um = 0.0, 1.0 >>> model.calc_qmdh_v1() >>> aides.qmdh qmdh(0.0, 0.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_QLV_QRV_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the discharge of both forelands after Manning-Strickler.
- Basic equation:
\(QV = MFV \cdot \frac{AV^{5/3}}{UV^{2/3}}\)
Examples:
Note the handling of zero values for
ULVandURV(in the second subsection):>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(2) >>> derived.mfv(left=10.0, right=18.0) >>> aides.alv = 3.0, 3.0 >>> aides.arv = 4.0, 4.0 >>> aides.ulv = 7.0, 0.0 >>> aides.urv = 8.0, 0.0 >>> model.calc_qlv_qrv_v1() >>> aides.qlv qlv(17.053102, 0.0) >>> aides.qrv qrv(45.357158, 0.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_QLV_QRV_V2[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the discharge of both forelands following the kinematic wave approach.
- Basic equation:
\(QV = \frac{QVDH}{AVDH} \cdot AV\)
Examples:
Note the handling of zero values for
ALVDHandARVDH(in the second subsection):>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(2) >>> aides.alv = 3.0, 3.0 >>> aides.arv = 5.0, 5.0 >>> aides.qlvdh = 4.0, 4.0 >>> aides.qrvdh = 6.0, 6.0 >>> aides.alvdh = 2.0, 0.0 >>> aides.arvdh = 4.0, 0.0 >>> model.calc_qlv_qrv_v2() >>> aides.qlv qlv(6.0, 0.0) >>> aides.qrv qrv(7.5, 0.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_QLVDH_QRVDH_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the derivative of both forelands’ discharge with respect to the stage following method
Calc_QLV_QRV_V1.- Basic equation:
\(QVDH = MFV \cdot \frac{5 \cdot AV^{2/3} \cdot AVDH}{3 \cdot UV^{2/3}} - \frac{2 \cdot AV^{5/3} \cdot UVDH}{3 \cdot UV^{5/3}}\)
Examples:
First, we apply the class
NumericalDifferentiatorto validate the calculated derivatives:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(2) >>> hm(1.0) >>> bv(left=2.0, right=3.0) >>> bnv(left=4.0, right=5.0) >>> derived.bnvf.update() >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=2.0) >>> derived.mfv(left=10.0, right=18.0) >>> derived.hrp(0.0) >>> states.h = 0.5, 1.5 >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> model.calc_alv_arv_ulv_urv_v1() >>> model.calc_alvdh_arvdh_ulvdh_urvdh_v1() >>> model.calc_qlvdh_qrvdh_v1() >>> aides.qlvdh qlvdh(0.0, 29.091363) >>> aides.qrvdh qrvdh(0.0, 74.651886)
>>> from hydpy import NumericalDifferentiator >>> numdiff = NumericalDifferentiator( ... xsequence=states.h, ... ysequences=[aides.qlv, aides.qrv], ... methods=[model.calc_rhv_v1, ... model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1, ... model.calc_alv_arv_ulv_urv_v1, ... model.calc_qlv_qrv_v1])() d_qlv/d_h: 0.0, 29.091363 d_qrv/d_h: 0.0, 74.651886
Second, we show that zero values for
ALVorULVas well as forARVorURVresult in zero values forQLVDHorQRVDH, respectively:>>> aides.alv = 1.0, 0.0 >>> aides.ulv = 0.0, 1.0 >>> aides.arv = 1.0, 0.0 >>> aides.urv = 0.0, 1.0 >>> model.calc_qlvdh_qrvdh_v1() >>> aides.qlvdh qlvdh(0.0, 0.0) >>> aides.qrvdh qrvdh(0.0, 0.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the discharge of both outer embankments after Manning-Strickler.
- Basic equation:
\(QVR = MFV \cdot \frac{AVR^{5/3}}{UVR^{2/3}}\)
Examples:
Note the handling of zero values for
ULVRandURVR(in the second subsection):>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(2) >>> derived.mfv(left=10.0, right=1.2) >>> aides.alvr = 3.0, 3.0 >>> aides.arvr = 4.0, 4.0 >>> aides.ulvr = 7.0, 0.0 >>> aides.urvr = 8.0, 0.0 >>> model.calc_qlvr_qrvr_v1() >>> aides.qlvr qlvr(17.053102, 0.0) >>> aides.qrvr qrvr(3.023811, 0.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V2[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the discharge of both outer embankments following the kinematic wave approach.
- Basic equation:
\(QVR = \frac{QVRDH}{AVRDH} \cdot AVR\)
Examples:
Note the handling of zero values for
ALVRDHandARVRDH(in the second subsection):>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(2) >>> aides.alvr = 3.0, 3.0 >>> aides.arvr = 5.0, 5.0 >>> aides.qlvrdh = 4.0, 4.0 >>> aides.qrvrdh = 6.0, 6.0 >>> aides.alvrdh = 2.0, 0.0 >>> aides.arvrdh = 4.0, 0.0 >>> model.calc_qlvr_qrvr_v2() >>> aides.qlvr qlvr(6.0, 0.0) >>> aides.qrvr qrvr(7.5, 0.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_QLVRDH_QRVRDH_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the derivative of the discharge over the outer embankments with respect to the stage following method
Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V1.- Basic equation:
\(QVRDH = MFVR \cdot \frac{5 \cdot AVR^{2/3} \cdot AVRDH}{3 \cdot UVR^{2/3}} - \frac{2 \cdot AVR{5/3} \cdot UVRDH}{3 \cdot UVR^{5/3}}\)
Examples:
First, we apply the class
NumericalDifferentiatorto validate the calculated derivatives:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(2) >>> hm(1.0) >>> bnvr(left=4.0, right=5.0) >>> derived.bnvrf.update() >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=2.0) >>> derived.mfv(left=10.0, right=18.0) >>> derived.hrp(0.0) >>> states.h = 1.5, 3.5 >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> model.calc_alvr_arvr_ulvr_urvr_v1() >>> model.calc_alvrdh_arvrdh_ulvrdh_urvrdh_v1() >>> model.calc_qlvrdh_qrvrdh_v1() >>> aides.qlvrdh qlvrdh(0.0, 64.717418) >>> aides.qrvrdh qrvrdh(0.0, 23.501747)
>>> from hydpy import NumericalDifferentiator >>> NumericalDifferentiator( ... xsequence=states.h, ... ysequences=[aides.qlvr, aides.qrvr], ... methods=[model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1, ... model.calc_alvr_arvr_ulvr_urvr_v1, ... model.calc_qlvr_qrvr_v1])() d_qlvr/d_h: 0.0, 64.717418 d_qrvr/d_h: 0.0, 23.501747
Second, we show that zero values for
ALVRorULVRas well as forARVRorURVRresult in zero values forQLVRDHorQRVRDH, respectively:>>> aides.alvr = 1.0, 0.0 >>> aides.ulvr = 0.0, 1.0 >>> aides.arvr = 1.0, 0.0 >>> aides.urvr = 0.0, 1.0 >>> model.calc_qlvrdh_qrvrdh_v1() >>> aides.qlvrdh qlvrdh(0.0, 0.0) >>> aides.qrvrdh qrvrdh(0.0, 0.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_AG_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the through wetted of the total cross-sections.
- Basic equation:
\(AG = AM+ALV+ARV+ALVR+ARVR\)
Example:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(2) >>> aides.am = 0.0, 1.0 >>> aides.alv = 2.0, 4.0 >>> aides.arv = 3.0, 5.0 >>> aides.alvr = 6.0, 8.0 >>> aides.arvr = 7.0, 9.0 >>> model.calc_ag_v1() >>> aides.ag ag(18.0, 27.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_QG_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the discharge of the total cross-section.
- Basic equation:
\(QG = QM + QLV + QRV + QLVR + QRVR\)
Example:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(2) >>> aides.qm = 0.0, 1.0 >>> aides.qlv = 2.0, 4.0 >>> aides.qrv = 3.0, 5.0 >>> aides.qlvr = 6.0, 8.0 >>> aides.qrvr = 7.0, 9.0 >>> model.calc_qg_v1() >>> fluxes.qg qg(18.0, 27.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_QG_V2[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the discharge of the total cross-section based on an interpolated flow velocity.
- Basic equation:
\(QG = EK \cdot \frac{1000 \cdot V_{interpolated} \cdot VG \cdot GTS}{Laen}\)
Example:
For simplicity, we define a linear between flow velocity and water storage:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(2) >>> laen(10.0) >>> ek(0.5) >>> vg2fg(PPoly.from_data(xs=[0.0, 1.0], ys=[0.0, 1.0])) >>> from hydpy import UnitTest >>> test = UnitTest(model, ... model.calc_qg_v2, ... last_example=3, ... parseqs=(states.vg, ... fluxes.qg)) >>> test.nexts.vg = numpy.empty((4, 2)) >>> test.nexts.vg[:, 0] = numpy.arange(-1.0, 3.0) >>> test.nexts.vg[:, 1] = numpy.arange(3.0, 7.0) >>> test() | ex. | vg | qg | ----------------------------------- | 1 | -1.0 3.0 | 0.0 900.0 | | 2 | 0.0 4.0 | 0.0 1600.0 | | 3 | 1.0 5.0 | 100.0 2500.0 |
Our example shows that a linear velocity-volume relationship results in a quadratic discharge-volume relationship. Note also that we generally set the discharge to zero for negative volumes.
For more realistic approximations of measured relationships between storage and discharge, we require larger neural networks.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_WBM_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the water table width above the main channel.
Examples:
Due to \(WBM = \frac{dAM}{dh}\), we can apply the class
NumericalDifferentiatorto validate the calculated water table widths:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(5) >>> bm(4.0) >>> bnm(2.0) >>> hm(1.0) >>> hr(0.0) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> states.h = 0.0, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1, 2.0 >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> model.calc_rhmdh_v1() >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> model.calc_wbm_v1() >>> aides.wbm wbm(4.0, 7.6, 8.0, 8.0, 8.0)
>>> from hydpy import NumericalDifferentiator >>> numdiff = NumericalDifferentiator( ... xsequence=states.h, ... ysequences=[aides.am], ... methods=[model.calc_rhm_v1, ... model.calc_rhv_v1, ... model.calc_am_um_v1]) >>> numdiff() d_am/d_h: 4.0, 7.6, 8.0, 8.0, 8.0
>>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> model.calc_rhmdh_v1() >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> model.calc_wbm_v1() >>> aides.wbm wbm(2.081965, 7.593774, 7.918034, 8.028465, 8.0)
>>> numdiff() d_am/d_h: 2.081965, 7.593774, 7.918034, 8.028465, 8.0
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_WBLV_WBRV_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the water table width above both forelands.
Examples:
Due to \(WBV = \frac{dAV}{dh}\), we can apply the class
NumericalDifferentiatorto validate the calculated water table widths:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(11) >>> bm(4.0) >>> bnm(2.0) >>> derived.bnvf.update() >>> hm(1.0) >>> bv(left=2.0, right=3.0) >>> bbv(left=10., right=40.) >>> bnv(left=10., right=20.) >>> derived.hv.update() >>> derived.hv hv(left=1.0, right=2.0) >>> hr(0.0) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> states.h = 1.0, 1.5, 1.9, 2.0, 2.1, 2.5, 2.9, 3.0, 3.1, 3.5, 4.0 >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> model.calc_wblv_wbrv_v1() >>> aides.wblv wblv(2.0, 7.0, 11.0, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0) >>> aides.wbrv wbrv(3.0, 13.0, 21.0, 23.0, 25.0, 33.0, 41.0, 43.0, 43.0, 43.0, 43.0)
>>> from hydpy import NumericalDifferentiator >>> numdiff = NumericalDifferentiator( ... xsequence=states.h, ... ysequences=[aides.alv, aides.arv], ... methods=[model.calc_rhv_v1, ... model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1, ... model.calc_alv_arv_ulv_urv_v1]) >>> numdiff() d_alv/d_h: 2.0, 7.0, 11.0, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0 d_arv/d_h: 3.0, 13.0, 21.0, 23.0, 25.0, 33.0, 41.0, 43.0, 43.0, 43.0, 43.0
>>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> model.calc_wblv_wbrv_v1() >>> aides.wblv wblv(1.204913, 6.998638, 10.984437, 11.795086, 12.071163, 12.000937, 12.000002, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0) >>> aides.wbrv wbrv(1.909826, 12.997489, 20.999995, 22.999999, 25.0, 33.0, 40.96888, 42.590174, 43.142325, 43.001873, 43.000001)
>>> numdiff() d_alv/d_h: 1.204913, 6.998638, 10.984437, 11.795086, 12.071163, 12.000937, 12.000002, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0, 12.0 d_arv/d_h: 1.909826, 12.997489, 20.999995, 22.999999, 25.0, 33.0, 40.96888, 42.590174, 43.142325, 43.001873, 43.000001
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_WBLVR_WBRVR_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the water table width above both outer embankments.
Examples:
Due to \(WBVR = \frac{dAVR}{dh}\), we can apply the class
NumericalDifferentiatorto validate the calculated water table widths:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(11) >>> hm(1.0) >>> bnvr(left=4.0, right=5.0) >>> derived.bnvrf.update() >>> derived.hv(left=1.0, right=2.0) >>> hr(0.0) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> states.h = 1.0, 1.5, 1.9, 2.0, 2.1, 2.5, 2.9, 3.0, 3.1, 3.5, 4.0 >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> model.calc_wblvr_wbrvr_v1() >>> aides.wblvr wblvr(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.4, 2.0, 3.6, 4.0, 4.4, 6.0, 8.0) >>> aides.wbrvr wbrvr(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 2.5, 5.0)
>>> from hydpy import NumericalDifferentiator >>> numdiff = NumericalDifferentiator( ... xsequence=states.h, ... ysequences=[aides.alvr, aides.arvr], ... methods=[model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1, ... model.calc_alvr_arvr_ulvr_urvr_v1]) >>> numdiff() d_alvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.4, 2.0, 3.6, 4.0, 4.4, 6.0, 8.0 d_arvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 2.5, 5.0
>>> hr(0.1) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> model.calc_wblvr_wbrvr_v1() >>> aides.wblvr wblvr(0.0, 0.0, 0.006224, 0.081965, 0.371535, 1.999625, 3.599999, 4.0, 4.4, 6.0, 8.0) >>> aides.wbrvr wbrvr(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.00778, 0.102457, 0.464419, 2.499532, 5.0)
>>> numdiff() d_alvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.006224, 0.081965, 0.371535, 1.999625, 3.599999, 4.0, 4.4, 6.0, 8.0 d_arvr/d_h: 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.00778, 0.102457, 0.464419, 2.499532, 5.0
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_WBG_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the water level width of the total cross-section.
- Basic equation:
\(WBG = WBM+WLV+WRV+WLVR+WRVR\)
Example:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(2) >>> aides.wbm = 0.0, 1.0 >>> aides.wblv = 2.0, 4.0 >>> aides.wbrv = 3.0, 5.0 >>> aides.wblvr = 6.0, 8.0 >>> aides.wbrvr = 7.0, 9.0 >>> model.calc_wbg_v1() >>> aides.wbg wbg(18.0, 27.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_DH_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodDetermine the change in the stage.
- Basic equation:
\(DH = \frac{QG_{i-1}-QG_i}{WBG \cdot 1000 \cdot Laen / GTS}\)
Example:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> laen(10.0) >>> gts(5) >>> aides.wbg(3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 3.5, 3.0) >>> fluxes.qz = 1.0 >>> fluxes.qg = 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 3.0, 2.0 >>> model.calc_dh_v1() >>> fluxes.dh dh(-0.000167, -0.000143, -0.000125, 0.000143, 0.000167)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Update_H_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodUpdate the stage.
- Basic equation:
\(\frac{dH}{dt} = DH\)
Example:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(5) >>> derived.sek(60*60) >>> fluxes.dh = -0.12, -0.1, -0.09, 0.1, 0.12 >>> fluxes.dh /= 60*60 >>> states.h(1.0, 1.2, 1.3, 1.2, 1.0) >>> model.update_h_v1() >>> states.h h(0.88, 1.1, 1.21, 1.3, 1.12)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Update_VG_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodUpdate the water volume.
- Basic equation:
\(\frac{dV}{dt} = QG_{i-1}-QG_i\)
Example:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(5) >>> derived.sek(60*60) >>> states.vg(1.0, 1.2, 1.3, 1.2, 1.0) >>> fluxes.qza = 1.0 >>> fluxes.qg = 3.0, 2.0, 4.0, 3.0, 5.0 >>> model.update_vg_v1() >>> states.vg vg(0.9928, 1.2036, 1.2928, 1.2036, 0.9928)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_QA_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodQuery the actual outflow.
Examples:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(3) >>> fluxes.qz = 1.0 >>> fluxes.qg = 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 >>> model.calc_qa_v1() >>> fluxes.qa qa(4.0) >>> gts(0) >>> model.calc_qa_v1() >>> fluxes.qa qa(1.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Update_WaterVolume_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodUpdate the old water volume with the current inflow.
- Requires the derived parameter:
- Requires the flux sequences:
- Updates the state sequence:
Examples:
Method
Update_WaterVolume_V1uses the value of sequenceInflowfor the first segment and the respective values of sequencesInternalFlowfor the remaining segments:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw_impl_euler import * >>> parameterstep() >>> nmbsegments(3) >>> derived.seconds(1e6) >>> states.watervolume.old = 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 >>> fluxes.inflow = 1.0 >>> fluxes.internalflow = 2.0, 3.0 >>> model.run_segments(model.update_watervolume_v1) >>> from hydpy import print_vector >>> print_vector(states.watervolume.old) 3.0, 5.0, 7.0
Negative inflow values are acceptable, even if they result in negative amounts of stored water:
>>> fluxes.inflow = -4.0 >>> fluxes.internalflow = -6.0, -6.0 >>> model.run_segments(model.update_watervolume_v1) >>> print_vector(states.watervolume.old) -1.0, -1.0, 1.0
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Return_InitialWaterVolume_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate and return the initial water volume that agrees with the given final water depth following the implicit Euler method.
- Required by the method:
- Requires the control parameters:
- Requires the derived parameter:
- Basic equation:
- \[\begin{split}A \cdot l / n \cdot 10^{-3} + Q \cdot s \cdot 10^{-6} \\ \\ d = waterdepth \\ A = f_{get\_wettedarea}(d) \\ l = Length \\ n = NmbSegments \\ Q = f_{get\_discharge}(d) \\ s = Seconds\end{split}\]
Examples:
The calculated initial volume is the sum of the water volume at the end of the simulation step and the outflow during the simulation step:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw_impl_euler import * >>> parameterstep() >>> length(100.0) >>> nmbsegments(10) >>> derived.seconds(60 * 60 * 24) >>> with model.add_wqmodel_v1("wq_trapeze_strickler"): ... nmbtrapezes(1) ... bottomlevels(1.0) ... bottomwidths(20.0) ... sideslopes(0.0) ... bottomslope(0.001) ... stricklercoefficients(30.0) ... calibrationfactors(1.0) >>> from hydpy import round_ >>> round_(model.return_initialwatervolume_v1(2.0)) 5.008867
If a segment has zero length, it can, of course, store no water. Hence, the returned value then only comprises the volume of the outflow of the current simulation step:
>>> length(0.0) >>> round_(model.return_initialwatervolume_v1(2.0)) 4.608867
Method
Return_InitialWaterVolume_V1handles cases where the number of segments is zero as if the channel’s length is zero (even if it is inconsistently set to a larger value):>>> length(100.0) >>> nmbsegments(0) >>> round_(model.return_initialwatervolume_v1(2.0)) 4.608867
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Return_VolumeError_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate and return the difference between the initial water volume that stems from the last simulation step plus the current inflow and the water volume that agrees with the given final water depth following the implicit Euler method.
- Required by the method:
- Required submethod:
- Requires the control parameters:
- Requires the derived parameter:
- Requires the state sequence:
- Basic equation:
- \[\begin{split}V_1 - V_2 \\ \\ V_1 = WaterVolume \\ V_2 = f_{Return\_InitialWaterVolume\_V1}(waterdepth)\end{split}\]
Examples:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw_impl_euler import * >>> parameterstep() >>> length(100.0) >>> nmbsegments(10) >>> derived.seconds(60 * 60 * 24) >>> with model.add_wqmodel_v1("wq_trapeze_strickler"): ... nmbtrapezes(1) ... bottomlevels(1.0) ... bottomwidths(20.0) ... sideslopes(0.0) ... bottomslope(0.001) ... stricklercoefficients(30.0) ... calibrationfactors(1.0) >>> states.watervolume(4.0) >>> from hydpy import round_ >>> round_(model.return_volumeerror_v1(2.0)) -1.008867
For a given water depth of zero,
Return_VolumeError_V1simply returns the old value ofWaterVolumeto safe computation efforts:>>> round_(model.return_volumeerror_v1(0.0)) 4.0
The following example shows that this simplification is correct:
>>> round_(model.return_volumeerror_v1(1e-6)) 4.0
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.PegasusImplicitEuler(model: Model)[source]¶
Bases:
PegasusPegasus iterator for determining the water level at the end of a simulation step.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_WaterDepth_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodDetermine the new water depth based on the implicit Euler method.
- Required submethod:
- Requires the control parameters:
- Requires the derived parameters:
- Requires the solver parameters:
- Requires the state sequence:
- Calculates the factor sequence:
Examples:
Compared to other (explicit) routing methods, the iterative approach of method
Calc_WaterDepth_V1to determine the final water depth for each river segment iteratively leads to high efficiency and (theoretically) absolute stability for short channel segments (namely, stiff problems with a high Courant number). However, be aware that the accuracy of this iteration affects the overall simulation. We begin demonstrating this with a single trapezoid and default numerical values:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw_impl_euler import * >>> parameterstep() >>> length(100.0) >>> nmbsegments(1) >>> with model.add_wqmodel_v1("wq_trapeze_strickler"): ... nmbtrapezes(1) ... bottomlevels(1.0) ... bottomwidths(20.0) ... sideslopes(0.0) ... bottomslope(0.001) ... stricklercoefficients(30.0) ... calibrationfactors(1.0) >>> derived.seconds(60 * 60 * 24) >>> derived.nmbdiscontinuities.update() >>> derived.finaldepth2initialvolume.update() >>> solver.watervolumetolerance.update() >>> solver.waterdepthtolerance.update() >>> model.idx_segment = 0
The following test function prints the resulting water depth for several initial volumes and also prints the water volume-related error tolerance (internally calculated as \(WaterVolumeTolerance \cdot InitialWaterVolume\)) and the actual error:
>>> from hydpy import print_vector >>> def check_search_algorithm(): ... print("volume", "depth", "tolerance", "error") ... for target_volume in (0.0, 0.1, 1.0, 2.0, 5.0, 10.0, 100.0): ... states.watervolume.old = target_volume ... model.calc_waterdepth_v1() ... depth = factors.waterdepth.values[0] ... volume = model.return_initialwatervolume_v1(depth) ... tolerance = solver.watervolumetolerance * target_volume ... error = target_volume - volume ... print_vector([target_volume, depth, tolerance, error])
All required and achieved accuracies are below the printed precisions:
>>> check_search_algorithm() volume depth tolerance error 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 0.1, 0.045296, 0.0, 0.0 1.0, 0.356485, 0.0, 0.0 2.0, 0.632911, 0.0, 0.0 5.0, 1.312357, 0.0, 0.0 10.0, 2.244486, 0.0, 0.0 100.0, 13.729876, 0.0, 0.0
If one wishes to improve accuracy or speed up the computation, it is preferable to decrease or increase
WaterVolumeTolerance. Here, we increase it and observe that higher numerical errors result:>>> solver.watervolumetolerance(1e-4) >>> check_search_algorithm() volume depth tolerance error 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 0.1, 0.045296, 0.00001, 0.0 1.0, 0.356498, 0.0001, -0.000042 2.0, 0.632912, 0.0002, -0.000004 5.0, 1.312356, 0.0005, 0.000004 10.0, 2.244563, 0.001, -0.000447 100.0, 13.729886, 0.01, -0.000091
Alternatively, one can modify the solver parameter
WaterDepthTolerance, whose value is used without any modification:>>> solver.watervolumetolerance(0.0) >>> solver.waterdepthtolerance(1e-2) >>> check_search_algorithm() volume depth tolerance error 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 0.1, 0.045296, 0.0, 0.0 1.0, 0.356498, 0.0, -0.000042 2.0, 0.632912, 0.0, -0.000004 5.0, 1.312356, 0.0, 0.000004 10.0, 2.244563, 0.0, -0.000447 100.0, 13.729876, 0.0, 0.0
Now, we define a profile geometry consisting of 3 stacked trapezes:
>>> with model.add_wqmodel_v1("wq_trapeze_strickler"): ... nmbtrapezes(3) ... bottomlevels(1.0, 3.0, 5.0) ... bottomwidths(20.0) ... sideslopes(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) ... bottomslope(0.001) ... stricklercoefficients(30.0) ... calibrationfactors(1.0) >>> derived.nmbdiscontinuities.update() >>> derived.finaldepth2initialvolume.update() >>> solver.watervolumetolerance.update() >>> solver.waterdepthtolerance.update()
Method
Calc_WaterDepth_V1uses the relevant bottom depths of these trapezes as boundaries for the Pegasus method so that the corresponding discontinuities cannot slow down its convergence:>>> check_search_algorithm() volume depth tolerance error 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 0.1, 0.045296, 0.0, 0.0 1.0, 0.356503, 0.0, -0.000059 2.0, 0.632918, 0.0, -0.000027 5.0, 1.312357, 0.0, 0.0 10.0, 2.170538, 0.0, 0.0 100.0, 7.624652, 0.0, -0.000004
In the last example, the default tolerance values result in practically likely irrelevant but still recognisable inaccuracies. The following example shows that decreasing the water depth-related tolerance reduces these errors:
>>> solver.waterdepthtolerance(1e-8) >>> check_search_algorithm() volume depth tolerance error 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 0.1, 0.045296, 0.0, 0.0 1.0, 0.356485, 0.0, 0.0 2.0, 0.632911, 0.0, 0.0 5.0, 1.312357, 0.0, 0.0 10.0, 2.170538, 0.0, 0.0 100.0, 7.624652, 0.0, 0.0
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Update_WaterVolume_V2[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the new water volume that agrees with the previously calculated final water depth.
- Requires the control parameters:
- Requires the factor sequence:
- Updates the state sequence:
- Basic equation:
- \[\begin{split}V = A \cdot l / n \cdot 10^{-3} \\ \\ V = WaterVolume \\ A = f_{get\_wettedarea}(D) \\ l = Length \\ n = NmbSegments\end{split}\]
Examples:
Note that, usually, the W-Q submodel must have been processed with the correct final water depth beforehand so that it can provide the related wetted area:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw_impl_euler import * >>> parameterstep() >>> length(100.0) >>> nmbsegments(1) >>> with model.add_wqmodel_v1("wq_trapeze_strickler"): ... nmbtrapezes(1) ... bottomlevels(1.0) ... sideslopes(0.0) ... calibrationfactors(1.0) >>> model.wqmodel.sequences.factors.wettedarea = 2.0 >>> model.idx_segment = 0 >>> model.update_watervolume_v2() >>> states.watervolume watervolume(0.2)
For zero water depths or channel lengths,
Update_WaterVolume_V2sets the final water volume to zero (independent of the submodel’s currentl wetted area):>>> model.wqmodel.sequences.factors.wettedarea = -999.0 >>> factors.waterdepth = 0.0 >>> model.update_watervolume_v2() >>> states.watervolume watervolume(0.0) >>> factors.waterdepth = 1.0 >>> length(0.0) >>> model.update_watervolume_v2() >>> states.watervolume watervolume(0.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_InternalFlow_Outflow_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate the flow out of the channel segments.
- Requires the control parameter:
- Requires the derived parameter:
- Requires the state sequence:
- Calculates the flux sequences:
- Basic equation:
- \[\begin{split}IO = (V_{old} - V_{new}) / s \cdot 1e6 \\ \\ IO = InternalFlow \ or Outflow \\ V = WaterVolume \\ s = Seconds\end{split}\]
Example:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw_impl_euler import * >>> parameterstep() >>> nmbsegments(3) >>> derived.seconds(1e6) >>> states.watervolume.old = 5.0, 2.0, 4.0 >>> states.watervolume.new = 1.0, 4.0, 2.0 >>> model.run_segments(model.calc_internalflow_outflow_v1) >>> fluxes.outflow outflow(2.0) >>> fluxes.internalflow internalflow(4.0, -2.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Calc_Outflow_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodTake the inflow as the outflow for channels zero-segment channels.
- Requires the control parameter:
- Requires the flux sequence:
- Calculates the flux sequence:
- Basic equation:
- \[Outflow = Inflow\]
Examples:
Method
Calc_Outflow_V1serves as a stopgap to ensure that the inflow is correctly passed to the outflow if a model does not contain any segments:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw_impl_euler import * >>> parameterstep() >>> fluxes.inflow = 1.0 >>> fluxes.outflow = 0.0
>>> nmbsegments(1) >>> model.calc_outflow_v1() >>> fluxes.outflow outflow(0.0)
>>> nmbsegments(0) >>> model.calc_outflow_v1() >>> fluxes.outflow outflow(1.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Pass_Q_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodPass the outflow to the outlet node.
Example:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> fluxes.qa = 2.0 >>> model.pass_q_v1() >>> outlets.q q(2.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Pass_Outflow_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodPass the outflow to the outlet node.
Example:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> fluxes.outflow = 2.0 >>> model.pass_outflow_v1() >>> outlets.q q(2.0)
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Return_QF_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate and return the “error” between the actual discharge and the discharge corresponding to the given water stage.
- Required by the method:
- Required submethods:
Calc_RHM_V1Calc_RHMDH_V1Calc_RHV_V1Calc_RHVDH_V1Calc_RHLVR_RHRVR_V1Calc_RHLVRDH_RHRVRDH_V1Calc_AM_UM_V1Calc_ALV_ARV_ULV_URV_V1Calc_ALVR_ARVR_ULVR_URVR_V1Calc_QM_V1Calc_QLV_QRV_V1Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V1Calc_AG_V1Calc_QG_V1- Requires the control parameters:
- Requires the derived parameters:
- Calculates the state sequence:
- Calculates the aide sequences:
RHMRHMDHRHVRHVDHRHLVRRHRVRRHLVRDHRHRVRDHAMUMALVARVULVURVALVRARVRULVRURVRQMQLVQRVQLVRQRVRAG
- Basic equation:
\(Q(H) - QG_0\)
Method
Return_QF_V1is a helper function not intended for performing simulation runs but for easing the implementation of methodcalculate_characteristiclength()of application modelkinw_williams(and similar functionalities). More specifically, it defines the target function for the iterative root search triggered by methodReturn_H_V1.While method
Return_QF_V1performs discharge calculations for all stream subsections, it evaluates only those of the first subsection. Accordingly, to avoid wasting computation time, one should not initialise more than one subsection before calling methodReturn_QF_V1(or methodsReturn_H_V1orcalculate_characteristiclength()).Example:
We reuse the example given in the main documentation on module
kinw_williams:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep("1d") >>> simulationstep("30m")
>>> gts(1) >>> laen(100.0) >>> gef(0.00025) >>> bm(15.0) >>> bnm(5.0) >>> skm(1.0/0.035) >>> hm(6.0) >>> bv(100.0) >>> bbv(20.0) >>> bnv(10.0) >>> bnvr(100.0) >>> skv(10.0) >>> ekm(1.0) >>> ekv(1.0) >>> hr(0.1) >>> parameters.update()
A water stage of 1 m results in a discharge of 7.7 m³/s:
>>> states.h = 1.0 >>> model.calc_rhm_v1() >>> model.calc_rhmdh_v1() >>> model.calc_rhv_v1() >>> model.calc_rhvdh_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() >>> model.calc_am_um_v1() >>> model.calc_alv_arv_ulv_urv_v1() >>> model.calc_alvr_arvr_ulvr_urvr_v1() >>> model.calc_qm_v1() >>> model.calc_qlv_qrv_v1() >>> model.calc_qlvr_qrvr_v1() >>> model.calc_ag_v1() >>> model.calc_qg_v1() >>> fluxes.qg qg(7.745345)
The calculated
QGvalue serves as the “true” value. Now, when passing stage values of 0.5 and 1.0 m, methodReturn_QF_V1calculates the corresponding discharge values and returns the “errors” -5.5 m³/s (a stage of 0.5 m results in a too-small discharge value) and 0.0 m³/s (1.0 m is the “true” stage), respectively:>>> from hydpy import round_ >>> round_(model.return_qf_v1(0.5)) -5.474691 >>> round_(model.return_qf_v1(1.0)) 0.0
Note that method
Return_QF_V1does not overwrite the first entry ofQG, which would complicate its application within an iterative approach.Technical checks:
Note that method
Return_QF_V1calculates the value of sequenceQGtemporarily and resets it afterwards, and calculates all other values of the mentioned sequences without resetting:>>> from hydpy.core.testtools import check_selectedvariables >>> from hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model import Return_QF_V1 >>> print(check_selectedvariables(Return_QF_V1)) Definitely missing: qg Possibly missing (REQUIREDSEQUENCES): Calc_RHM_V1: H Calc_RHMDH_V1: H Calc_RHV_V1: H Calc_RHVDH_V1: H Calc_RHLVR_RHRVR_V1: H Calc_RHLVRDH_RHRVRDH_V1: H Calc_AM_UM_V1: RHM and RHV Calc_ALV_ARV_ULV_URV_V1: RHV, RHLVR, and RHRVR Calc_ALVR_ARVR_ULVR_URVR_V1: RHLVR and RHRVR Calc_QM_V1: AM and UM Calc_QLV_QRV_V1: ALV, ARV, ULV, and URV Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V1: ALVR, ARVR, ULVR, and URVR Calc_AG_V1: AM, ALV, ARV, ALVR, and ARVR Calc_QG_V1: QM, QLV, QRV, QLVR, and QRVR Possibly missing (RESULTSEQUENCES): Calc_QG_V1: QG
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.Return_H_V1[source]¶
Bases:
MethodCalculate and return the water stage corresponding to the current discharge value.
Method
Return_H_V1is a helper function not for performing simulation runs but for easing the implementation of methodcalculate_characteristiclength()of application modelkinw_williams(or similar functionalities). It performs a root search by applying thePegasusmethod implemented in module rootutils on the target methodReturn_QF_V1. Hence, please see the additional application notes in the documentation on methodReturn_QF_V1.Example:
We recreate the exact parameterisation as in the example of the documentation on method
Return_QF_V1:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> simulationstep("30m") >>> parameterstep()
>>> gts(1) >>> laen(100.0) >>> gef(0.00025) >>> bm(15.0) >>> bnm(5.0) >>> skm(1.0/0.035) >>> hm(6.0) >>> bv(100.0) >>> bbv(20.0) >>> bnv(10.0) >>> bnvr(100.0) >>> skv(10.0) >>> ekm(1.0) >>> ekv(1.0) >>> hr(0.1) >>> parameters.update()
For a given discharge value of 7.7 m³/s (discussed in the documentation on method
Return_QF_V1), methodReturn_H_V1correctly determines the water stage of 1 m:>>> fluxes.qg = 7.745345 >>> from hydpy import print_vector, round_ >>> round_(model.return_h_v1()) 1.0
To evaluate our implementation’s reliability, we search for water stages covering an extensive range of discharge values. The last printed column shows that method
Return_H_V1finds the correct water stage in all cases:>>> import numpy >>> for q in [0.0]+list(numpy.logspace(-6, 6, 13)): ... fluxes.qg = q ... h = model.return_h_v1() ... states.h = h ... model.calc_rhm_v1() ... model.calc_rhmdh_v1() ... model.calc_rhv_v1() ... model.calc_rhvdh_v1() ... model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() ... model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() ... model.calc_am_um_v1() ... model.calc_alv_arv_ulv_urv_v1() ... model.calc_alvr_arvr_ulvr_urvr_v1() ... model.calc_qm_v1() ... model.calc_qlv_qrv_v1() ... model.calc_qlvr_qrvr_v1() ... model.calc_ag_v1() ... model.calc_qg_v1() ... error = fluxes.qg[0]-q ... print_vector([q, h, error]) 0.0, -10.0, 0.0 0.000001, -0.390737, 0.0 0.00001, -0.308934, 0.0 0.0001, -0.226779, 0.0 0.001, -0.143209, 0.0 0.01, -0.053833, 0.0 0.1, 0.061356, 0.0 1.0, 0.310079, 0.0 10.0, 1.150307, 0.0 100.0, 3.717833, 0.0 1000.0, 9.108276, 0.0 10000.0, 18.246131, 0.0 100000.0, 37.330632, 0.0 1000000.0, 81.363979, 0.0
Due to smoothing the water stage with respect to the channel bottom, small discharge values result in negative water stages. The lowest allowed stage is -10 m.
Through setting the regularisation parameter
HRto zero (which we do not recommend), methodReturn_H_V1should return the non-negative water stages agreeing with the original, discontinuous Manning-Strickler equation:>>> hr(0.0) >>> parameters.update() >>> for q in [0.0]+list(numpy.logspace(-6, 6, 13)): ... fluxes.qg = q ... h = model.return_h_v1() ... states.h = h ... model.calc_rhm_v1() ... model.calc_rhmdh_v1() ... model.calc_rhv_v1() ... model.calc_rhvdh_v1() ... model.calc_rhlvr_rhrvr_v1() ... model.calc_rhlvrdh_rhrvrdh_v1() ... model.calc_am_um_v1() ... model.calc_alv_arv_ulv_urv_v1() ... model.calc_alvr_arvr_ulvr_urvr_v1() ... model.calc_qm_v1() ... model.calc_qlv_qrv_v1() ... model.calc_qlvr_qrvr_v1() ... model.calc_ag_v1() ... model.calc_qg_v1() ... error = fluxes.qg[0]-q ... print_vector([q, h, error]) 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 0.000001, 0.00008, 0.0 0.00001, 0.000317, 0.0 0.0001, 0.001263, 0.0 0.001, 0.005027, 0.0 0.01, 0.019992, 0.0 0.1, 0.079286, 0.0 1.0, 0.31039, 0.0 10.0, 1.150307, 0.0 100.0, 3.717833, 0.0 1000.0, 9.108276, 0.0 10000.0, 18.246131, 0.0 100000.0, 37.330632, 0.0 1000000.0, 81.363979, 0.0
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.PegasusH(model: Model)[source]¶
Bases:
PegasusPegasus iterator for finding the correct water stage.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_model.BaseModelProfile[source]¶
Bases:
ELSModelBase class for HydPy-KinW models performing discharge calculations based on a triple trapezoid profile.
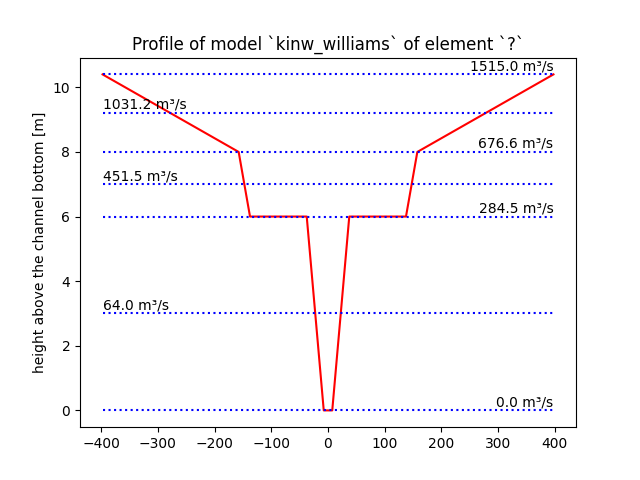
- plot_profile(labelformat: str = '%.1f') None[source]¶
Plot the triple trapezoid profile and insert the discharge values at some distinct stages.
We reuse the second example given in the main documentation on module
kinw_williams:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw_williams import * >>> parameterstep("1d") >>> simulationstep("30m") >>> laen(100.0) >>> gef(0.00025) >>> bm(15.0) >>> bnm(5.0) >>> skm(1.0/0.035) >>> hm(6.0) >>> bv(100.0) >>> bbv(20.0) >>> bnv(10.0) >>> bnvr(100.0) >>> skv(10.0) >>> ekm(1.0) >>> ekv(1.0) >>> hr(0.1) >>> gts(1) >>> parameters.update()
Calling method
plot_profile()prepares the profile plot and, depending on your matplotlib configuration, eventually prints it directly on your screen:>>> model.plot_profile() >>> from hydpy.core.testtools import save_autofig >>> save_autofig("kinw_plot_profile.png")
- prepare_hvector(nmb: int = 1000, exp: float = 2.0, hmin: float | None = None, hmax: float | None = None) tuple[float, ...][source]¶
Prepare a vector of the stage values.
The argument nmb defines the number of stage values, exp defines their spacing (1.0 results in equidistant values), and hmin and hmax the lowest and highest water stage, respectively:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw_williams import * >>> parameterstep() >>> from hydpy import print_vector >>> print_vector(model.prepare_hvector( ... nmb=10, hmin=-1.0, hmax=8, exp=1.0)) -1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0
When not specified by the user, method
prepare_hvector()determines hmin and hmax based on the current value ofHM(-10 % and 300 %, respectively) and takes a higher sampling rate in the lower value range (by setting exp to two):>>> hm(6.0) >>> print_vector(model.prepare_hvector(nmb=10)) -0.6, -0.37037, 0.318519, 1.466667, 3.074074, 5.140741, 7.666667, 10.651852, 14.096296, 18.0
- calculate_qgvector(hvector: Iterable[float]) tuple[float, ...][source]¶
Calculate the discharge values (in m³/s) corresponding to the given stage vector.
We reuse the second example given in the main documentation on module
kinw_williamsalso show the results of the similar methodscalculate_agvector()andcalculate_vgvector():>>> from hydpy.models.kinw_williams import * >>> parameterstep("1d") >>> simulationstep("30m") >>> laen(100.0) >>> gef(0.00025) >>> bm(15.0) >>> bnm(5.0) >>> skm(1.0/0.035) >>> hm(6.0) >>> bv(100.0) >>> bbv(20.0) >>> bnv(10.0) >>> bnvr(100.0) >>> skv(10.0) >>> ekm(1.0) >>> ekv(1.0) >>> hr(0.1) >>> gts(2) >>> parameters.update()
>>> from hydpy import print_vector >>> print_vector(model.calculate_qgvector([0.0, 1.0, 2.0])) 0.033153, 7.745345, 28.436875 >>> print_vector(model.calculate_agvector([0.0, 1.0, 2.0])) 0.623138, 20.0, 50.0 >>> print_vector(model.calculate_vgvector([0.0, 1.0, 2.0])) 0.031157, 1.0, 2.5
- calculate_agvector(hvector: Iterable[float]) tuple[float, ...][source]¶
Calculate the wetted cross-section areas (in m²) corresponding to the given vector of stage values.
See the documentation on method
calculate_qgvector()for an example.
- REUSABLE_METHODS = ()¶
Parameter Features¶
Control parameters¶
- class hydpy.models.kinw.ControlParameters(master: Parameters, cls_fastaccess: type[FastAccessParameter] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)
Bases:
ControlParametersControl parameters of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
Laen()Flusslänge (channel length) [km].Length()Channel length [km].Gef()Sohlgefälle (channel slope) [-].GTS()Anzahl Gewässerteilstrecken (number of channel subsections) [-].NmbSegments()Number of channel segments [-].HM()Höhe Hauptgerinne (height of the main channel) [m].BM()Sohlbreite Hauptgerinne (bed width of the main channel) [m].BNM()Böschungsneigung Hauptgerinne (slope of both main channel embankments) [-].BV()Sohlbreite Vorländer (bed widths of both forelands) [m].BBV()Breite Vorlandböschungen (width of both foreland embankments) [m].BNV()Böschungsneigung Vorländer (slope of both foreland embankments) [-].BNVR()Böschungsneigung Vorlandränder (slope of both outer embankments) [-].SKM()Rauigkeitsbeiwert Hauptgerinne (roughness coefficient of the main channel) [m^(1/3)/s].SKV()Rauigkeitsbeiwert Vorländer (roughness coefficient of both forelands) [m^(1/3)/s].EKM()Kalibrierfaktor Hauptgerinne (calibration factor for the main channel) [-].EKV()Kalibrierfaktor Vorländer (calibration factor for both forelands) [m].HR()Allgemeiner Glättungsparameter für den Wasserstand (general smoothing parameter for the water stage) [mm].VG2FG()Flexibler Interpolator zur Berechnung der Fließgeschwindigkeit in Abhängigkeit zur aktuellen Wasserspeicherung einer Gewässerteilstrecke (flexible interpolator describing the relationship between the flow velocity and the water storage of individual channel subsections) [m/s].EK()Kalibrierfaktor (calibration factor) [-].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.Laen(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterFlusslänge (channel length) [km].
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'laen'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'km'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.Length(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterChannel length [km].
- Required by the methods:
Calc_WaterDepth_V1Return_InitialWaterVolume_V1Return_VolumeError_V1Update_WaterVolume_V2
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'length'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'km'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.Gef(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterSohlgefälle (channel slope) [-].
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'gef'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = '-'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.GTS(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterAnzahl Gewässerteilstrecken (number of channel subsections) [-].
- Required by the methods:
Calc_AG_V1Calc_ALVDH_ARVDH_ULVDH_URVDH_V1Calc_ALVRDH_ARVRDH_ULVRDH_URVRDH_V1Calc_ALVR_ARVR_ULVR_URVR_V1Calc_ALV_ARV_ULV_URV_V1Calc_AMDH_UMDH_V1Calc_AM_UM_V1Calc_DH_V1Calc_QA_V1Calc_QG_V1Calc_QG_V2Calc_QLVDH_QRVDH_V1Calc_QLVRDH_QRVRDH_V1Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V1Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V2Calc_QLV_QRV_V1Calc_QLV_QRV_V2Calc_QMDH_V1Calc_QM_V1Calc_QM_V2Calc_RHLVRDH_RHRVRDH_V1Calc_RHLVR_RHRVR_V1Calc_RHMDH_V1Calc_RHM_V1Calc_RHVDH_V1Calc_RHV_V1Calc_WBG_V1Calc_WBLVR_WBRVR_V1Calc_WBLV_WBRV_V1Calc_WBM_V1Return_H_V1Return_QF_V1Update_H_V1Update_VG_V1
Calling the parameter
GTSprepares the shape of all 1-dimensional sequences for which each entry corresponds to an individual channel subsection:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> gts(3) >>> states.h h(nan, nan, nan)
- SPAN = (0, None)¶
- name = 'gts'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = '-'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.NmbSegments(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
NmbParameterNumber of channel segments [-].
NmbSegmentsprepares the shape of some 1-dimensional sequences automatically:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> nmbsegments(2) >>> nmbsegments nmbsegments(2) >>> states.watervolume.shape (2,) >>> factors.waterdepth.shape (2,) >>> fluxes.internalflow.shape (1,)
NmbSegmentspreserves existing values if the number of segments does not change:>>> states.watervolume = 1.0, 2.0 >>> nmbsegments(2) >>> states.watervolume watervolume(1.0, 2.0)
Setting its value to zero is allowed:
>>> nmbsegments(0) >>> states.watervolume.shape (0,) >>> fluxes.internalflow.shape (0,)
- SPAN = (0, None)¶
- name = 'nmbsegments'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = '-'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.HM(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterHöhe Hauptgerinne (height of the main channel) [m].
- Required by the methods:
Calc_RHLVRDH_RHRVRDH_V1Calc_RHLVR_RHRVR_V1Calc_RHVDH_V1Calc_RHV_V1Return_H_V1Return_QF_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'hm'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.BM(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterSohlbreite Hauptgerinne (bed width of the main channel) [m].
- Required by the methods:
Calc_AMDH_UMDH_V1Calc_AM_UM_V1Calc_WBM_V1Return_H_V1Return_QF_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'bm'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.BNM(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterBöschungsneigung Hauptgerinne (slope of both main channel embankments) [-].
- Required by the methods:
Calc_AMDH_UMDH_V1Calc_AM_UM_V1Calc_WBM_V1Return_H_V1Return_QF_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'bnm'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = '-'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.BV(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
LeftRightParameterSohlbreite Vorländer (bed widths of both forelands) [m].
- Required by the methods:
Calc_ALVDH_ARVDH_ULVDH_URVDH_V1Calc_ALV_ARV_ULV_URV_V1Calc_WBLV_WBRV_V1Return_H_V1Return_QF_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'bv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.BBV(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
LeftRightParameterBreite Vorlandböschungen (width of both foreland embankments) [m].
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'bbv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.BNV(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
LeftRightParameterBöschungsneigung Vorländer (slope of both foreland embankments) [-].
- Required by the methods:
Calc_ALVDH_ARVDH_ULVDH_URVDH_V1Calc_ALV_ARV_ULV_URV_V1Calc_WBLV_WBRV_V1Return_H_V1Return_QF_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'bnv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = '-'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.BNVR(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
LeftRightParameterBöschungsneigung Vorlandränder (slope of both outer embankments) [-].
- Required by the methods:
Calc_ALVRDH_ARVRDH_ULVRDH_URVRDH_V1Calc_ALVR_ARVR_ULVR_URVR_V1Calc_WBLVR_WBRVR_V1Return_H_V1Return_QF_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'bnvr'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = '-'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.SKM(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterRauigkeitsbeiwert Hauptgerinne (roughness coefficient of the main channel) [m^(1/3)/s].
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'skm'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm^(1/3)/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.SKV(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
LeftRightParameterRauigkeitsbeiwert Vorländer (roughness coefficient of both forelands) [m^(1/3)/s].
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'skv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm^(1/3)/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.EKM(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterKalibrierfaktor Hauptgerinne (calibration factor for the main channel) [-].
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'ekm'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = '-'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.EKV(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
LeftRightParameterKalibrierfaktor Vorländer (calibration factor for both forelands) [m].
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'ekv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.HR(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterAllgemeiner Glättungsparameter für den Wasserstand (general smoothing parameter for the water stage) [mm].
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'hr'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'mm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_control.VG2FG(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
SimpleInterpolatorFlexibler Interpolator zur Berechnung der Fließgeschwindigkeit in Abhängigkeit zur aktuellen Wasserspeicherung einer Gewässerteilstrecke (flexible interpolator describing the relationship between the flow velocity and the water storage of individual channel subsections) [m/s].
- Required by the method:
You can configure the velocity-storage relationship with all functionalities provided by classes
ANNandPPoly. Here, we define a small neural network:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep() >>> vg2fg(ANN(weights_input=-1.0, weights_output=0.4, ... intercepts_hidden=0.0, intercepts_output=0.2)) >>> vg2fg vg2fg( ANN( weights_input=[[-1.0]], weights_output=[[0.4]], intercepts_hidden=[[0.0]], intercepts_output=[0.2], ) ) >>> vg2fg.print_table([0.0, 1.0, inf]) x y dy/dx 0.0 0.4 -0.1 1.0 0.307577 -0.078645 inf 0.2 0.0
If you prefer a constant velocity, you can set it directly via the keyword velocity (its unit must be m/s):
>>> vg2fg(velocity=1.0) >>> vg2fg vg2fg(velocity=1.0) >>> vg2fg.print_table([0.0, 1.0]) x y dy/dx 0.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 0.0
Alternatively, the keyword timedelay allows for defining the flow velocity via the number of hours it takes for a flood wave to travel through the whole channel:
>>> laen(100.0) >>> vg2fg(timedelay=27.77778) >>> vg2fg vg2fg(timedelay=27.77778)
>>> vg2fg.inputs[0] = 0.0 >>> vg2fg.calculate_values() >>> vg2fg.print_table([0.0, 1.0]) x y dy/dx 0.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 0.0
The same time delay indicates a ten times slower flow velocity for a ten times shorter channel:
>>> laen(10.0) >>> vg2fg(timedelay=27.77778) >>> vg2fg vg2fg(timedelay=27.77778) >>> vg2fg.print_table([0.0, 1.0]) x y dy/dx 0.0 0.1 0.0 1.0 0.1 0.0
You must supply precisely one argument:
>>> vg2fg() Traceback (most recent call last): ... ValueError: parameter `vg2fg` of element `?` requires exactly one argument but `0` are given.
- XLABEL = 'VG [million m³]'¶
- YLABEL = 'FG [m/s]'¶
Derived parameters¶
- class hydpy.models.kinw.DerivedParameters(master: Parameters, cls_fastaccess: type[FastAccessParameter] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)
Bases:
DerivedParametersDerived parameters of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
Sek()Sekunden im Simulationszeitschritt (Number of seconds of the selected simulation time step) [s].Seconds()The length of the actual simulation step size in seconds [s].HV()Höhe Vorländer (height of both forelands) [m].MFM()Produkt der zeitkonstanten Terme der Manning-Strickler-Formel für das Hauptgerinne (product of the time-constant terms of the Manning-Strickler equation, calculated for the main channel) [m^(1/3)/s].MFV()Produkt der zeitkonstanten Terme der Manning-Strickler-Formel für beide Vorländer (product of the time-constant terms of the Manning-Strickler equation, calculated for both forelands) [m^(1/3)/s].BNMF()Hilfsterm zur Berechnung des benetzten Böschungsumfangs im Hauptgerinne (auxiliary term for the calculation of the wetted perimeter of the slope of the main channel) [m].BNVF()Hilfsterm zur Berechnung des benetzten Böschungsumfangs der Vorländer (auxiliary term for the calculation of the wetted perimeter of the slope of both forelands) [m].BNVRF()Hilfsterm zur Berechnung des benetzten Böschungsumfangs der Vorlandränder (auxiliary term for the calculation of the wetted perimeter of the slope of both outer embankments) [m].HRP()Wasserstand-Regularisierungs-Parameter zur Verwendung in Verbindung mit Regularisierungsfunktionsmooth_logistic2()(regularisation parameter for water stage to be used when applying regularisation functionsmooth_logistic2()) [m].NmbDiscontinuities()Number of points of discontinuity in the rating curve [-].FinalDepth2InitialVolume()A pair of the final water depth and the corresponding initial water volume according to the implicit Euler method for each point of discontinuity in the rating curve [m and million m³].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_derived.Sek(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
SecondsParameterSekunden im Simulationszeitschritt (Number of seconds of the selected simulation time step) [s].
- Required by the methods:
- name = 'sek'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 's'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_derived.Seconds(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
SecondsParameterThe length of the actual simulation step size in seconds [s].
- Required by the methods:
Calc_InternalFlow_Outflow_V1Calc_WaterDepth_V1Return_InitialWaterVolume_V1Return_VolumeError_V1Update_WaterVolume_V1
- name = 'seconds'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 's'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_derived.HV(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
LeftRightParameterHöhe Vorländer (height of both forelands) [m].
- Required by the methods:
Calc_RHLVRDH_RHRVRDH_V1Calc_RHLVR_RHRVR_V1Return_H_V1Return_QF_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- update() None[source]¶
Update based on \(HV=BBV/BNV\).
- Examples:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep("1d") >>> bbv(left=10., right=40.) >>> bnv(left=10., right=20.) >>> derived.hv.update() >>> derived.hv hv(left=1.0, right=2.0) >>> bbv(left=10., right=0.) >>> bnv(left=0., right=20.) >>> derived.hv.update() >>> derived.hv hv(0.0)
- name = 'hv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_derived.MFM(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterProdukt der zeitkonstanten Terme der Manning-Strickler-Formel für das Hauptgerinne (product of the time-constant terms of the Manning-Strickler equation, calculated for the main channel) [m^(1/3)/s].
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- update() None[source]¶
Update based on \(MFM=EKM \cdot SKM \cdot \sqrt{Gef}\).
- Examples:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep("1d") >>> ekm(2.0) >>> skm(50.0) >>> gef(0.01) >>> derived.mfm.update() >>> derived.mfm mfm(10.0)
- name = 'mfm'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm^(1/3)/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_derived.MFV(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
LeftRightParameterProdukt der zeitkonstanten Terme der Manning-Strickler-Formel für beide Vorländer (product of the time-constant terms of the Manning-Strickler equation, calculated for both forelands) [m^(1/3)/s].
- Required by the methods:
Calc_QLVDH_QRVDH_V1Calc_QLVRDH_QRVRDH_V1Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V1Calc_QLV_QRV_V1Return_H_V1Return_QF_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- update() None[source]¶
Update based on \(MFV=EKV \cdot SKV \cdot \sqrt{Gef}\).
- Examples:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep("1d") >>> ekv(left=2.0, right=4.0) >>> skv(left=25.0, right=50) >>> gef(0.01) >>> derived.mfv.update() >>> derived.mfv mfv(left=5.0, right=20.0)
- name = 'mfv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm^(1/3)/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_derived.BNMF(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterHilfsterm zur Berechnung des benetzten Böschungsumfangs im Hauptgerinne (auxiliary term for the calculation of the wetted perimeter of the slope of the main channel) [m].
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- update() None[source]¶
Update based on \(BNMF= \sqrt{1+BNM^2}\).
- Examples:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep("1d") >>> bnm(2.0) >>> derived.bnmf.update() >>> derived.bnmf bnmf(2.236068)
- name = 'bnmf'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_derived.BNVF(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
LeftRightParameterHilfsterm zur Berechnung des benetzten Böschungsumfangs der Vorländer (auxiliary term for the calculation of the wetted perimeter of the slope of both forelands) [m].
- Required by the methods:
Calc_ALVDH_ARVDH_ULVDH_URVDH_V1Calc_ALV_ARV_ULV_URV_V1Return_H_V1Return_QF_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- update() None[source]¶
Update based on \(BNVF= \sqrt{1+BNV^2}\).
- Examples:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep("1d") >>> bnv(left=2.0, right=3.0) >>> derived.bnvf.update() >>> derived.bnvf bnvf(left=2.236068, right=3.162278)
- name = 'bnvf'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_derived.BNVRF(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
LeftRightParameterHilfsterm zur Berechnung des benetzten Böschungsumfangs der Vorlandränder (auxiliary term for the calculation of the wetted perimeter of the slope of both outer embankments) [m].
- Required by the methods:
Calc_ALVRDH_ARVRDH_ULVRDH_URVRDH_V1Calc_ALVR_ARVR_ULVR_URVR_V1Return_H_V1Return_QF_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- update() None[source]¶
Update based on \(BNVRF= \sqrt(1+BNVR^2)\).
- Examples:
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> parameterstep("1d") >>> bnvr(left=2.0, right=3.0) >>> derived.bnvrf.update() >>> derived.bnvrf bnvrf(left=2.236068, right=3.162278)
- name = 'bnvrf'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_derived.HRP(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterWasserstand-Regularisierungs-Parameter zur Verwendung in Verbindung mit Regularisierungsfunktion
smooth_logistic2()(regularisation parameter for water stage to be used when applying regularisation functionsmooth_logistic2()) [m].- Required by the methods:
Calc_RHLVRDH_RHRVRDH_V1Calc_RHLVR_RHRVR_V1Calc_RHMDH_V1Calc_RHM_V1Calc_RHVDH_V1Calc_RHV_V1Return_H_V1Return_QF_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- update() None[source]¶
Calculate the smoothing parameter value.
The documentation on module
smoothtoolsexplains the following example in some detail:>>> from hydpy.models.kinw import * >>> from hydpy.cythons.smoothutils import smooth_logistic2 >>> from hydpy import round_ >>> parameterstep() >>> hr(0.0) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> round_(smooth_logistic2(0.0, derived.hrp)) 0.0 >>> hr(2.5) >>> derived.hrp.update() >>> round_(smooth_logistic2(2.5, derived.hrp)) 2.51
- name = 'hrp'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_derived.NmbDiscontinuities(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterNumber of points of discontinuity in the rating curve [-].
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0, None)¶
- update() None[source]¶
Take the number of discontinuities from the available cross-section submodel.
>>> from hydpy.models.kinw_impl_euler import * >>> parameterstep() >>> derived.nmbdiscontinuities.update() Traceback (most recent call last): ... hydpy.core.exceptiontools.AttributeNotReady: Submodel `wqmodel` is required for updating parameter `nmbdiscontinuities` of element `?`, but is still not available.
>>> with model.add_wqmodel_v1("wq_trapeze_strickler"): ... nmbtrapezes(2) ... bottomlevels(1.0, 3.0) ... bottomslope(0.01) ... sideslopes(2.0, 4.0) ... calibrationfactors(1.0) >>> derived.nmbdiscontinuities.update() >>> derived.nmbdiscontinuities nmbdiscontinuities(1)
- name = 'nmbdiscontinuities'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = '-'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_derived.FinalDepth2InitialVolume(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
ParameterA pair of the final water depth and the corresponding initial water volume according to the implicit Euler method for each point of discontinuity in the rating curve [m and million m³].
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- update() None[source]¶
Use the methods
get_depths_of_discontinuity()andReturn_InitialWaterVolume_V1to determine the final water depths and the corresponding initial water volumes.>>> from hydpy.models.kinw_impl_euler import * >>> parameterstep() >>> length(100.0) >>> nmbsegments(10) >>> derived.seconds(60 * 60 * 24) >>> derived.nmbdiscontinuities(2) >>> derived.finaldepth2initialvolume.update() Traceback (most recent call last): ... hydpy.core.exceptiontools.AttributeNotReady: Submodel `wqmodel` is required for updating parameter `finaldepth2initialvolume` of element `?`, but is still not available.
>>> with model.add_wqmodel_v1("wq_trapeze_strickler"): ... nmbtrapezes(3) ... bottomlevels(1.0, 3.0, 5.0) ... bottomwidths(20.0) ... sideslopes(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) ... bottomslope(0.001) ... stricklercoefficients(30.0) ... calibrationfactors(1.0) >>> derived.finaldepth2initialvolume.update() >>> derived.finaldepth2initialvolume finaldepth2initialvolume([[2.0, 5.008867], [4.0, 19.01208]])
- name = 'finaldepth2initialvolume'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm and million m³'¶
Unit of the variable.
Fixed parameters¶
- class hydpy.models.kinw.FixedParameters(master: Parameters, cls_fastaccess: type[FastAccessParameter] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)
Bases:
FixedParametersFixed parameters of model kinw.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_fixed.WBMin(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
FixedParameterMindestwert der Wasserspiegelbreite (minimum value of the water level width [m].
- Required by the method:
In theory, the value of
WBMinshould always be zero. However, at least the numerical implementation of application modelkinw_williamsrequires a value slightly lower than zero for reasons of numerical stability when the simulated river section is dry.- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- INIT = 1e-09¶
- name = 'wbmin'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_fixed.WBReg(subvars: SubParameters)[source]¶
Bases:
FixedParameterAuf
WBMinbezogener effektiver Glättungsparameter (effectiv smoothing parameter related toWBMin) [m].- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- INIT = 1e-05¶
- name = 'wbreg'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
Solver parameters¶
- class hydpy.models.kinw.SolverParameters(master: Parameters, cls_fastaccess: type[FastAccessParameter] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)
Bases:
SolverParametersSolver parameters of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
NmbRuns()The number of (repeated) runs of theRUN_METHODSper simulation step [-].AbsErrorMax()Absolute numerical error tolerance [m³/s].RelErrorMax()Relative numerical error tolerance [-].RelDTMin()Smallest relative integration time step size allowed [-].RelDTMax()Largest relative integration time step size allowed [-].WaterVolumeTolerance()Targeted accuracy in terms of the relative water volume for the Pegasus search of the final water depth [-].WaterDepthTolerance()Targeted accuracy in terms of the absolute water depth for the Pegasus search of the final water depth [m].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_solver.NmbRuns(subvars)[source]¶
Bases:
SolverParameterThe number of (repeated) runs of the
RUN_METHODSper simulation step [-].- INIT = 1¶
- name = 'nmbruns'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = '-'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_solver.AbsErrorMax(subvars)[source]¶
Bases:
SolverParameterAbsolute numerical error tolerance [m³/s].
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- INIT = 1e-06¶
- name = 'abserrormax'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_solver.RelErrorMax(subvars)[source]¶
Bases:
SolverParameterRelative numerical error tolerance [-].
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- INIT = 0.001¶
- name = 'relerrormax'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = '-'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_solver.RelDTMin(subvars)[source]¶
Bases:
SolverParameterSmallest relative integration time step size allowed [-].
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- INIT = 0.0¶
- name = 'reldtmin'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = '-'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_solver.RelDTMax(subvars)[source]¶
Bases:
SolverParameterLargest relative integration time step size allowed [-].
- SPAN = (0.0, 1.0)¶
- INIT = 1.0¶
- name = 'reldtmax'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = '-'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_solver.WaterVolumeTolerance(subvars)[source]¶
Bases:
SolverParameterTargeted accuracy in terms of the relative water volume for the Pegasus search of the final water depth [-].
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- INIT = 1e-10¶
- name = 'watervolumetolerance'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = '-'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_solver.WaterDepthTolerance(subvars)[source]¶
Bases:
SolverParameterTargeted accuracy in terms of the absolute water depth for the Pegasus search of the final water depth [m].
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- INIT = 1e-10¶
- name = 'waterdepthtolerance'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
Sequence Features¶
Factor sequences¶
- class hydpy.models.kinw.FactorSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)
Bases:
FactorSequencesFactor sequences of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
WaterDepth()Water depth [m].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_factors.WaterDepth(subvars: ModelIOSequences[TM_co, ModelIOSequence, FastAccessIOSequence])[source]¶
Bases:
FactorSequenceWater depth [m].
- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'waterdepth'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
Flux sequences¶
- class hydpy.models.kinw.FluxSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)
Bases:
FluxSequencesFlux sequences of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
QZ()Mittlerer Zufluss in Gerinnestrecke (average inflow into the channel) [m³/s].QZA()Aktueller Zufluss in Gerinnestrecke (current inflow into the channel) [m³/s].Inflow()Flow into the first channel segment [m³/s].QG()Durchfluss gesamt (total discharge) [m³/s].InternalFlow()Flow between the channel segments [m³/s].QA()Abfluss aus Gerinnestrecke (outflow out of the channel) [m³/s].Outflow()Flow out of the last channel segment [m³/s].DH()Wasserstandänderung (temporal change of the water stage) [m/s].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_fluxes.QZ(subvars: ModelIOSequences[TM_co, ModelIOSequence, FastAccessIOSequence])[source]¶
Bases:
FluxSequenceMittlerer Zufluss in Gerinnestrecke (average inflow into the channel) [m³/s].
- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qz'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_fluxes.QZA(subvars: ModelIOSequences[TM_co, ModelIOSequence, FastAccessIOSequence])[source]¶
Bases:
FluxSequenceAktueller Zufluss in Gerinnestrecke (current inflow into the channel) [m³/s].
- Required by the method:
- NUMERIC = True¶
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qza'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_fluxes.Inflow(subvars: ModelIOSequences[TM_co, ModelIOSequence, FastAccessIOSequence])[source]¶
Bases:
FluxSequenceFlow into the first channel segment [m³/s].
- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the methods:
- name = 'inflow'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_fluxes.QG(subvars: ModelIOSequences[TM_co, ModelIOSequence, FastAccessIOSequence])[source]¶
Bases:
FluxSequenceDurchfluss gesamt (total discharge) [m³/s].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
- NUMERIC = True¶
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qg'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_fluxes.InternalFlow(subvars: ModelIOSequences[TM_co, ModelIOSequence, FastAccessIOSequence])[source]¶
Bases:
FluxSequenceFlow between the channel segments [m³/s].
- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- name = 'internalflow'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_fluxes.QA(subvars: ModelIOSequences[TM_co, ModelIOSequence, FastAccessIOSequence])[source]¶
Bases:
FluxSequenceAbfluss aus Gerinnestrecke (outflow out of the channel) [m³/s].
- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- NUMERIC = True¶
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qa'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_fluxes.Outflow(subvars: ModelIOSequences[TM_co, ModelIOSequence, FastAccessIOSequence])[source]¶
Bases:
FluxSequenceFlow out of the last channel segment [m³/s].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the method:
- name = 'outflow'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_fluxes.DH(subvars: ModelIOSequences[TM_co, ModelIOSequence, FastAccessIOSequence])[source]¶
Bases:
FluxSequenceWasserstandänderung (temporal change of the water stage) [m/s].
- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- NUMERIC = True¶
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'dh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
State sequences¶
- class hydpy.models.kinw.StateSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)
Bases:
StateSequencesState sequences of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
H()Wasserstand (water stage) [m].VG()Wasservolumen (water volume) [million m³].WaterVolume()Water volume [million m³].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_states.H(subvars: ModelIOSequences[TM_co, ModelIOSequence, FastAccessIOSequence])[source]¶
Bases:
StateSequenceWasserstand (water stage) [m].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Updated by the method:
- Required by the methods:
Calc_RHLVRDH_RHRVRDH_V1Calc_RHLVR_RHRVR_V1Calc_RHMDH_V1Calc_RHM_V1Calc_RHVDH_V1Calc_RHV_V1
- NUMERIC = True¶
- name = 'h'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_states.VG(subvars: ModelIOSequences[TM_co, ModelIOSequence, FastAccessIOSequence])[source]¶
Bases:
StateSequenceWasservolumen (water volume) [million m³].
- Updated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- NUMERIC = True¶
- name = 'vg'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'million m³'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_states.WaterVolume(subvars: ModelIOSequences[TM_co, ModelIOSequence, FastAccessIOSequence])[source]¶
Bases:
StateSequenceWater volume [million m³].
- Updated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
Calc_InternalFlow_Outflow_V1Calc_WaterDepth_V1Return_VolumeError_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'watervolume'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'million m³'¶
Unit of the variable.
Inlet sequences¶
- class hydpy.models.kinw.InletSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)
Bases:
InletSequencesInlet sequences of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
Q()Abfluss (runoff) [m³/s].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_inlets.Q(subvars: ModelIOSequences[TM_co, ModelIOSequence, FastAccessIOSequence])[source]¶
Bases:
InletSequenceAbfluss (runoff) [m³/s].
- Required by the methods:
- name = 'q'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
Outlet sequences¶
- class hydpy.models.kinw.OutletSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)
Bases:
OutletSequencesOutlet sequences of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
Q()Abfluss (runoff) [m³/s].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_outlets.Q(subvars: ModelIOSequences[TM_co, ModelIOSequence, FastAccessIOSequence])[source]¶
Bases:
OutletSequenceAbfluss (runoff) [m³/s].
- Calculated by the methods:
- name = 'q'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
Aide sequences¶
- class hydpy.models.kinw.AideSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)
Bases:
AideSequencesAide sequences of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
WBM()Wasserspiegelbreite Hauptgerinne (water level width of the main channel) [m].WBLV()Wasserspiegelbreite des linken Vorlandes (water level width of the left foreland) [m].WBRV()Wasserspiegelbreite des rechten Vorlandes (water level width of the right foreland) [m].WBLVR()Wasserspiegelbreite des linken Vorlandrandes (water level width of the left outer embankment) [m].WBRVR()Wasserspiegelbreite des rechten Vorlandrandes (water level width of the right outer embankment) [m].WBG()Wasserspiegelbreite des gesamten Querschnittes (water level width of the total cross section) [m].AM()Durchflossene Fläche Hauptgerinne (wetted area of the main channel) [m²].ALV()Durchflossene Fläche linkes Vorland (wetted area of the left foreland) [m²].ARV()Durchflossene Fläche rechtes Vorland (wetted area of the right foreland) [m²].ALVR()Durchflossene Fläche linker Vorlandrand (wetted area of the left outer embankments) [m²].ARVR()Durchflossene Fläche rechter Vorlandrand (wetted area of the right outer embankments) [m²].AG()Durchflossene Fläche gesamt (total wetted area) [m²].UM()Benetzter Umfang Hauptgerinne (wetted perimeter of the main channel) [m].ULV()Benetzter Umfang linkes Vorland (wetted perimeter of the left foreland) [m].URV()Benetzter Umfang rechtes Vorland (wetted perimeter of the right foreland) [m].ULVR()Benetzter Umfang linker Vorlandrand (wetted perimeter of the left outer embankment) [m].URVR()Benetzter Umfang rechtes Vorlandrand (wetted perimeter of the right outer embankment) [m].QM()Durchfluss Hauptgerinne (discharge of the main channel) [m³/s].QLV()Durchfluss linkes Vorland (discharge of the left foreland) [m³/s].QRV()Durchfluss rechtes Vorland (discharge of the right foreland) [m³/s].QLVR()Durchfluss linker Vorlandrand (discharge of the left outer embankment) [m³/s].QRVR()Durchfluss rechter Vorlandrand (discharge of the right outer embankment) [m³/s].RHM()Hinsichtlich der Gewässersohle regularisierter Wasserstand (stage regularised with respect to the channel bottom) [m].RHV()Hinsichtlich der des Übergangs Hauptgerinne/Vorländer regularisierter Wasserstand (stage regularised with respect to the transition from the main channel to both forelands) [m].RHLVR()Hinsichtlich der des Übergangs linkes Vorland/ linker Vorlandrand regularisierter Wasserstand (stage regularised with respect to the transition from the left foreland to the left outer embankment) [m].RHRVR()Hinsichtlich der des Übergangs rechtes Vorland/ rechter Vorlandrand regularisierter Wasserstand (stage regularised with respect to the transition from the right foreland to the right outer embankment) [m].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.WBM(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceWasserspiegelbreite Hauptgerinne (water level width of the main channel) [m].
- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'wbm'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.WBLV(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceWasserspiegelbreite des linken Vorlandes (water level width of the left foreland) [m].
- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'wblv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.WBRV(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceWasserspiegelbreite des rechten Vorlandes (water level width of the right foreland) [m].
- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'wbrv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.WBLVR(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceWasserspiegelbreite des linken Vorlandrandes (water level width of the left outer embankment) [m].
- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'wblvr'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.WBRVR(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceWasserspiegelbreite des rechten Vorlandrandes (water level width of the right outer embankment) [m].
- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'wbrvr'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.WBG(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceWasserspiegelbreite des gesamten Querschnittes (water level width of the total cross section) [m].
- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'wbg'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.AM(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceDurchflossene Fläche Hauptgerinne (wetted area of the main channel) [m²].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'am'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm²'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.ALV(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceDurchflossene Fläche linkes Vorland (wetted area of the left foreland) [m²].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
Calc_AG_V1Calc_QLVDH_QRVDH_V1Calc_QLV_QRV_V1Calc_QLV_QRV_V2
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'alv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm²'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.ARV(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceDurchflossene Fläche rechtes Vorland (wetted area of the right foreland) [m²].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
Calc_AG_V1Calc_QLVDH_QRVDH_V1Calc_QLV_QRV_V1Calc_QLV_QRV_V2
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'arv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm²'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.ALVR(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceDurchflossene Fläche linker Vorlandrand (wetted area of the left outer embankments) [m²].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
Calc_AG_V1Calc_QLVRDH_QRVRDH_V1Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V1Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V2
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'alvr'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm²'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.ARVR(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceDurchflossene Fläche rechter Vorlandrand (wetted area of the right outer embankments) [m²].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
Calc_AG_V1Calc_QLVRDH_QRVRDH_V1Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V1Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V2
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'arvr'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm²'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.AG(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceDurchflossene Fläche gesamt (total wetted area) [m²].
- Calculated by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'ag'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm²'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.UM(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceBenetzter Umfang Hauptgerinne (wetted perimeter of the main channel) [m].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'um'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.ULV(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceBenetzter Umfang linkes Vorland (wetted perimeter of the left foreland) [m].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'ulv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.URV(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceBenetzter Umfang rechtes Vorland (wetted perimeter of the right foreland) [m].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'urv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.ULVR(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceBenetzter Umfang linker Vorlandrand (wetted perimeter of the left outer embankment) [m].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'ulvr'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.URVR(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceBenetzter Umfang rechtes Vorlandrand (wetted perimeter of the right outer embankment) [m].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'urvr'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.QM(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceDurchfluss Hauptgerinne (discharge of the main channel) [m³/s].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qm'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.QLV(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceDurchfluss linkes Vorland (discharge of the left foreland) [m³/s].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qlv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.QRV(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceDurchfluss rechtes Vorland (discharge of the right foreland) [m³/s].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qrv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.QVR(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceDurchfluss Vorlandränder (discharge of both outer embankment) [m³/s].
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qvr'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.QLVR(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceDurchfluss linker Vorlandrand (discharge of the left outer embankment) [m³/s].
- Calculated by the methods:
Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V1Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V2Return_H_V1Return_QF_V1- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qlvr'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.QRVR(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceDurchfluss rechter Vorlandrand (discharge of the right outer embankment) [m³/s].
- Calculated by the methods:
Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V1Calc_QLVR_QRVR_V2Return_H_V1Return_QF_V1- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qrvr'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/s'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.RHM(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceHinsichtlich der Gewässersohle regularisierter Wasserstand (stage regularised with respect to the channel bottom) [m].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'rhm'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.RHMDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
RHM(derivative ofRHM) [m/m].- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'rhmdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.RHV(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceHinsichtlich der des Übergangs Hauptgerinne/Vorländer regularisierter Wasserstand (stage regularised with respect to the transition from the main channel to both forelands) [m].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
Calc_ALVDH_ARVDH_ULVDH_URVDH_V1Calc_ALV_ARV_ULV_URV_V1Calc_AMDH_UMDH_V1Calc_AM_UM_V1Calc_WBLV_WBRV_V1Calc_WBM_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'rhv'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.RHVDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
RHV(derivative ofRHV) [m/m].- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
Calc_ALVDH_ARVDH_ULVDH_URVDH_V1Calc_AMDH_UMDH_V1Calc_WBLV_WBRV_V1Calc_WBM_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'rhvdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.RHLVR(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceHinsichtlich der des Übergangs linkes Vorland/ linker Vorlandrand regularisierter Wasserstand (stage regularised with respect to the transition from the left foreland to the left outer embankment) [m].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
Calc_ALVDH_ARVDH_ULVDH_URVDH_V1Calc_ALVRDH_ARVRDH_ULVRDH_URVRDH_V1Calc_ALVR_ARVR_ULVR_URVR_V1Calc_ALV_ARV_ULV_URV_V1Calc_WBLVR_WBRVR_V1Calc_WBLV_WBRV_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'rhlvr'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.RHLVRDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
RHLVR(derivative ofRHLVR) [m/m].- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
Calc_ALVDH_ARVDH_ULVDH_URVDH_V1Calc_ALVRDH_ARVRDH_ULVRDH_URVRDH_V1Calc_WBLVR_WBRVR_V1Calc_WBLV_WBRV_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'rhlvrdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.RHRVR(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceHinsichtlich der des Übergangs rechtes Vorland/ rechter Vorlandrand regularisierter Wasserstand (stage regularised with respect to the transition from the right foreland to the right outer embankment) [m].
- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
Calc_ALVDH_ARVDH_ULVDH_URVDH_V1Calc_ALVRDH_ARVRDH_ULVRDH_URVRDH_V1Calc_ALVR_ARVR_ULVR_URVR_V1Calc_ALV_ARV_ULV_URV_V1Calc_WBLVR_WBRVR_V1Calc_WBLV_WBRV_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'rhrvr'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.RHRVRDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
RHRVR(derivative ofRHRVR) [m/m].- Calculated by the methods:
- Required by the methods:
Calc_ALVDH_ARVDH_ULVDH_URVDH_V1Calc_ALVRDH_ARVRDH_ULVRDH_URVRDH_V1Calc_WBLVR_WBRVR_V1Calc_WBLV_WBRV_V1
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'rhrvrdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.AMDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
AM(derivative ofAM) [m²/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'amdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm²/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.ALVDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
ALV(derivative ofALV) [m²/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'alvdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm²/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.ARVDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
ARV(derivative ofARV) [m²/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'arvdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm²/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.ALVRDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
ALVR(derivative ofALVR) [m²/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'alvrdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm²/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.ARVRDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
ARVR(derivative ofARVR) [m²/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the methods:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'arvrdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm²/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.UMDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
UM(derivative ofUM) [m/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'umdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.ULVDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
ULV(derivative ofULV) [m/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'ulvdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.URVDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
URV(derivative ofURV) [m/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'urvdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.ULVRDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
ULVR(derivative ofULVR) [m/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'ulvrdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.URVRDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
URVR(derivative ofURVR) [m/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'urvrdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.QMDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
QM(derivative ofQM) [m³/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qmdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.QLVDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
QLV(derivative ofQLV) [m³/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qlvdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.QRVDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
QRV(derivative ofQRV) [m³/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qrvdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.QLVRDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
QLVR(derivative ofQLVR) [m³/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qlvrdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.kinw_aides.QRVRDH(subvars: ModelSequences[modeltools.Model, ModelSequence, variabletools.FastAccess])[source]¶
Bases:
AideSequenceAbleitung von
QRVR(derivative ofQRVR) [m³/m].- Calculated by the method:
- Required by the method:
- SPAN = (0.0, None)¶
- name = 'qrvrdh'¶
Name of the variable in lowercase letters.
- unit = 'm³/m'¶
Unit of the variable.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.AideSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
AideSequencesAide sequences of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
WBM()Wasserspiegelbreite Hauptgerinne (water level width of the main channel) [m].WBLV()Wasserspiegelbreite des linken Vorlandes (water level width of the left foreland) [m].WBRV()Wasserspiegelbreite des rechten Vorlandes (water level width of the right foreland) [m].WBLVR()Wasserspiegelbreite des linken Vorlandrandes (water level width of the left outer embankment) [m].WBRVR()Wasserspiegelbreite des rechten Vorlandrandes (water level width of the right outer embankment) [m].WBG()Wasserspiegelbreite des gesamten Querschnittes (water level width of the total cross section) [m].AM()Durchflossene Fläche Hauptgerinne (wetted area of the main channel) [m²].ALV()Durchflossene Fläche linkes Vorland (wetted area of the left foreland) [m²].ARV()Durchflossene Fläche rechtes Vorland (wetted area of the right foreland) [m²].ALVR()Durchflossene Fläche linker Vorlandrand (wetted area of the left outer embankments) [m²].ARVR()Durchflossene Fläche rechter Vorlandrand (wetted area of the right outer embankments) [m²].AG()Durchflossene Fläche gesamt (total wetted area) [m²].UM()Benetzter Umfang Hauptgerinne (wetted perimeter of the main channel) [m].ULV()Benetzter Umfang linkes Vorland (wetted perimeter of the left foreland) [m].URV()Benetzter Umfang rechtes Vorland (wetted perimeter of the right foreland) [m].ULVR()Benetzter Umfang linker Vorlandrand (wetted perimeter of the left outer embankment) [m].URVR()Benetzter Umfang rechtes Vorlandrand (wetted perimeter of the right outer embankment) [m].QM()Durchfluss Hauptgerinne (discharge of the main channel) [m³/s].QLV()Durchfluss linkes Vorland (discharge of the left foreland) [m³/s].QRV()Durchfluss rechtes Vorland (discharge of the right foreland) [m³/s].QLVR()Durchfluss linker Vorlandrand (discharge of the left outer embankment) [m³/s].QRVR()Durchfluss rechter Vorlandrand (discharge of the right outer embankment) [m³/s].RHM()Hinsichtlich der Gewässersohle regularisierter Wasserstand (stage regularised with respect to the channel bottom) [m].RHV()Hinsichtlich der des Übergangs Hauptgerinne/Vorländer regularisierter Wasserstand (stage regularised with respect to the transition from the main channel to both forelands) [m].RHLVR()Hinsichtlich der des Übergangs linkes Vorland/ linker Vorlandrand regularisierter Wasserstand (stage regularised with respect to the transition from the left foreland to the left outer embankment) [m].RHRVR()Hinsichtlich der des Übergangs rechtes Vorland/ rechter Vorlandrand regularisierter Wasserstand (stage regularised with respect to the transition from the right foreland to the right outer embankment) [m].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.ControlParameters(master: Parameters, cls_fastaccess: type[FastAccessParameter] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
ControlParametersControl parameters of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
Laen()Flusslänge (channel length) [km].Length()Channel length [km].Gef()Sohlgefälle (channel slope) [-].GTS()Anzahl Gewässerteilstrecken (number of channel subsections) [-].NmbSegments()Number of channel segments [-].HM()Höhe Hauptgerinne (height of the main channel) [m].BM()Sohlbreite Hauptgerinne (bed width of the main channel) [m].BNM()Böschungsneigung Hauptgerinne (slope of both main channel embankments) [-].BV()Sohlbreite Vorländer (bed widths of both forelands) [m].BBV()Breite Vorlandböschungen (width of both foreland embankments) [m].BNV()Böschungsneigung Vorländer (slope of both foreland embankments) [-].BNVR()Böschungsneigung Vorlandränder (slope of both outer embankments) [-].SKM()Rauigkeitsbeiwert Hauptgerinne (roughness coefficient of the main channel) [m^(1/3)/s].SKV()Rauigkeitsbeiwert Vorländer (roughness coefficient of both forelands) [m^(1/3)/s].EKM()Kalibrierfaktor Hauptgerinne (calibration factor for the main channel) [-].EKV()Kalibrierfaktor Vorländer (calibration factor for both forelands) [m].HR()Allgemeiner Glättungsparameter für den Wasserstand (general smoothing parameter for the water stage) [mm].VG2FG()Flexibler Interpolator zur Berechnung der Fließgeschwindigkeit in Abhängigkeit zur aktuellen Wasserspeicherung einer Gewässerteilstrecke (flexible interpolator describing the relationship between the flow velocity and the water storage of individual channel subsections) [m/s].EK()Kalibrierfaktor (calibration factor) [-].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.DerivedParameters(master: Parameters, cls_fastaccess: type[FastAccessParameter] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
DerivedParametersDerived parameters of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
Sek()Sekunden im Simulationszeitschritt (Number of seconds of the selected simulation time step) [s].Seconds()The length of the actual simulation step size in seconds [s].HV()Höhe Vorländer (height of both forelands) [m].MFM()Produkt der zeitkonstanten Terme der Manning-Strickler-Formel für das Hauptgerinne (product of the time-constant terms of the Manning-Strickler equation, calculated for the main channel) [m^(1/3)/s].MFV()Produkt der zeitkonstanten Terme der Manning-Strickler-Formel für beide Vorländer (product of the time-constant terms of the Manning-Strickler equation, calculated for both forelands) [m^(1/3)/s].BNMF()Hilfsterm zur Berechnung des benetzten Böschungsumfangs im Hauptgerinne (auxiliary term for the calculation of the wetted perimeter of the slope of the main channel) [m].BNVF()Hilfsterm zur Berechnung des benetzten Böschungsumfangs der Vorländer (auxiliary term for the calculation of the wetted perimeter of the slope of both forelands) [m].BNVRF()Hilfsterm zur Berechnung des benetzten Böschungsumfangs der Vorlandränder (auxiliary term for the calculation of the wetted perimeter of the slope of both outer embankments) [m].HRP()Wasserstand-Regularisierungs-Parameter zur Verwendung in Verbindung mit Regularisierungsfunktionsmooth_logistic2()(regularisation parameter for water stage to be used when applying regularisation functionsmooth_logistic2()) [m].NmbDiscontinuities()Number of points of discontinuity in the rating curve [-].FinalDepth2InitialVolume()A pair of the final water depth and the corresponding initial water volume according to the implicit Euler method for each point of discontinuity in the rating curve [m and million m³].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.FactorSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
FactorSequencesFactor sequences of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
WaterDepth()Water depth [m].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.FixedParameters(master: Parameters, cls_fastaccess: type[FastAccessParameter] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
FixedParametersFixed parameters of model kinw.
- class hydpy.models.kinw.FluxSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
FluxSequencesFlux sequences of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
QZ()Mittlerer Zufluss in Gerinnestrecke (average inflow into the channel) [m³/s].QZA()Aktueller Zufluss in Gerinnestrecke (current inflow into the channel) [m³/s].Inflow()Flow into the first channel segment [m³/s].QG()Durchfluss gesamt (total discharge) [m³/s].InternalFlow()Flow between the channel segments [m³/s].QA()Abfluss aus Gerinnestrecke (outflow out of the channel) [m³/s].Outflow()Flow out of the last channel segment [m³/s].DH()Wasserstandänderung (temporal change of the water stage) [m/s].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.InletSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
InletSequencesInlet sequences of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
Q()Abfluss (runoff) [m³/s].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.OutletSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
OutletSequencesOutlet sequences of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
Q()Abfluss (runoff) [m³/s].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.SolverParameters(master: Parameters, cls_fastaccess: type[FastAccessParameter] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
SolverParametersSolver parameters of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
NmbRuns()The number of (repeated) runs of theRUN_METHODSper simulation step [-].AbsErrorMax()Absolute numerical error tolerance [m³/s].RelErrorMax()Relative numerical error tolerance [-].RelDTMin()Smallest relative integration time step size allowed [-].RelDTMax()Largest relative integration time step size allowed [-].WaterVolumeTolerance()Targeted accuracy in terms of the relative water volume for the Pegasus search of the final water depth [-].WaterDepthTolerance()Targeted accuracy in terms of the absolute water depth for the Pegasus search of the final water depth [m].
- class hydpy.models.kinw.StateSequences(master: Sequences, cls_fastaccess: type[TypeFastAccess_co] | None = None, cymodel: CyModelProtocol | None = None)¶
Bases:
StateSequencesState sequences of model kinw.
- The following classes are selected:
H()Wasserstand (water stage) [m].VG()Wasservolumen (water volume) [million m³].WaterVolume()Water volume [million m³].
